Pediatric vs. Adult CPR: Understanding the Key Differences in Resuscitation for Infants and Children
When an emergency strikes, time is the single most critical factor, and knowing how to administer Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is an absolute superpower. However, the world of resuscitation is not one-size-fits-all. A technique perfect for an adult could be harmful to a child, and an approach suitable for a child might be ineffective for an infant.
Understanding the subtle yet vital differences between adult, child, and infant CPR is what separates general knowledge from life-saving expertise. These variations are not arbitrary; they are rooted in the fundamental physiological and anatomical changes that occur as a human body grows. We will explore these critical distinctions, ensuring you are prepared to act with confidence and precision, regardless of the victim’s age.
What age markers define an Adult, Child, and Infant in CPR training?
CPR guidelines establish specific age parameters to ensure the correct technique and force are applied to the victim. These classifications are based on physiological development rather than strictly chronological age. Misidentifying a victim’s age category is one of the most common mistakes made by untrained rescuers.
The American Heart Association (AHA) and similar governing bodies use clear physical and developmental markers to determine which resuscitation protocol to follow.
- Infant: This category applies to any victim under the age of one year.
- Infants possess the most fragile anatomy, requiring the gentlest touch and a unique compression method.
- Child: This category is defined as a victim ranging from one year old up to the onset of puberty.
- Puberty is the key marker here; in females, this is often marked by breast development, and in males, by the presence of axillary (underarm) hair.
- If a victim looks small but shows signs of puberty, they should be treated using the adult protocol.
- Adult: This category includes any victim showing signs of puberty and older.
- If you are unsure whether a person is a large child or a small adult, always err on the side of caution.
- If the victim is large and physically mature, the adult protocol should be initiated.
Accurate age assessment is the very first step in determining which set of life-saving skills to deploy.
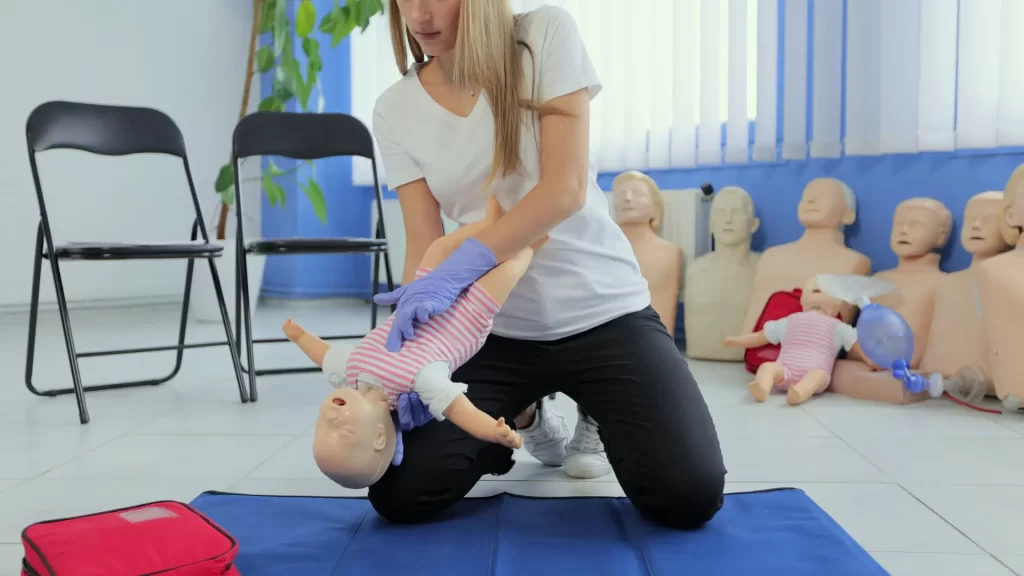

Why do the CPR techniques fundamentally change between age groups?
The reason CPR techniques must be adapted is simple: the underlying cause of cardiac arrest differs dramatically between adults and children. Understanding the root cause informs whether you should prioritize pumping blood or delivering oxygen.
The body’s mechanism of failure is what dictates the initial response strategy.
- Cardiac Arrest in Adults: The Electrical/Pumping Problem.
- In over 80% of adult cardiac arrests, the primary cause is a sudden, unexpected cardiac event.
- This is typically due to a heart attack, where the electrical system malfunctions, causing the heart to quiver uselessly (ventricular fibrillation).
- The lungs often still contain residual oxygen, so the immediate priority is performing deep, forceful chest compressions.
- Compressions circulate the remaining oxygenated blood to the brain and vital organs until an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) can correct the electrical problem.
- Cardiac Arrest in Children and Infants: The Breathing Problem.
- The majority of cardiac arrests in pediatric patients are secondary to respiratory failure.
- This is often caused by accidents like drowning, choking, severe asthma, trauma, or severe illness.
- When breathing stops, the body’s oxygen reserves are quickly depleted, causing the heart to slow down and eventually stop.
- Therefore, the primary goal of pediatric resuscitation is to re-oxygenate the victim.
- Rescue breaths become equally, if not more, important than compressions in the initial stages of pediatric CPR.
This difference in etiology is the philosophical bedrock upon which all technical distinctions in pediatric versus adult CPR are built.
How does the initial assessment procedure differ for adults versus children and infants?
While the initial sequence, Check, Call, Care, is universal, the method of checking responsiveness and the timing of calling emergency services vary based on age and whether the collapse was witnessed. This protocol ensures the fastest appropriate intervention.
Proper assessment begins with checking the victim and the environment.
- Checking Responsiveness:
- Adult: The rescuer should firmly tap the victim’s shoulder and shout, “Are you okay?“
- Child: A firm tap and verbal question are usually appropriate, but the force should be adjusted for size.
- Infant: Shaking is strictly prohibited due to the risk of brain injury. The rescuer should gently tap the baby’s foot or chest to check for a reaction.
- Activation of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) – The “Call First vs. Care First” Rule:
- Witnessed Collapse (Any Age): If the collapse is seen, it suggests a sudden, electrical cardiac problem. The priority is immediate EMS activation (call 911/emergency services) and retrieval of an AED.
- Unwitnessed Collapse (Adult): Assume a primary cardiac event. The lone rescuer should Call First, activate EMS immediately, get an AED, and then start CPR.
- Unwitnessed Collapse (Child or Infant): Assume a respiratory problem where time is needed for oxygenation. The lone rescuer must perform Care First, give two minutes (approximately five cycles) of CPR before leaving the victim to call 911/emergency services and retrieve an AED.
This critical difference in activation protocols reflects the need to treat the most likely cause of arrest first, maximizing the chance of survival for the age group involved.
What is the correct compression depth for an adult, child, and infant?
The force and depth of chest compressions are arguably the most critical variable in determining the effectiveness of CPR. Too shallow, and blood won’t circulate; too deep, and internal organs or bones could be damaged. Compression depth is calculated based on the victim’s size to ensure the heart is adequately squeezed.
The depth requirements for effective compressions change significantly based on the victim’s size and bone structure:
- Adult Compression Depth: For adults, the recommended depth is at least 2 inches (5 cm), but no more than 2.4 inches (6 cm). This level of force is necessary to depress the rigid adult sternum and effectively squeeze the heart against the spine to circulate blood.
- Child Compression Depth: The target depth for a child is about 2 inches (5 cm). More importantly, this should be approximately one-third the depth of the child’s chest. Their bones are softer than an adult’s, requiring less overall force, but the depth must be sufficient to ensure blood flow.
- Infant Compression Depth: The gentlest depth is required for infants, at about 1.5 inches (4 cm), which is also approximately one-third the depth of the chest. This minimal depth avoids injury to the infant’s delicate, pliable ribcage while still achieving effective circulation.
It is crucial for rescuers to maintain the correct depth while ensuring full chest recoil after every compression. Recoil allows the heart to refill with blood, making the next compression effective.
How does hand placement vary for chest compressions across all three groups?
The method used to apply force changes significantly based on the victim’s size to optimize depth and minimize the risk of injury. Hand placement ensures the force is applied to the lower half of the sternum, avoiding the delicate xiphoid process at the bottom of the breastbone.
The technique must be adjusted to the victim’s body mass and physical structure.
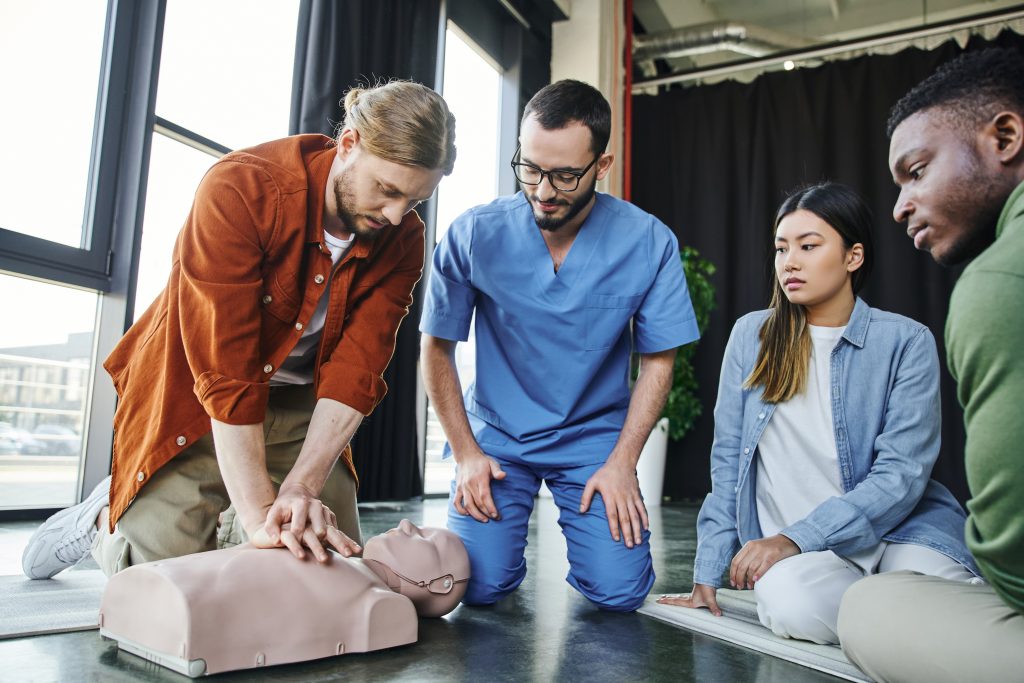
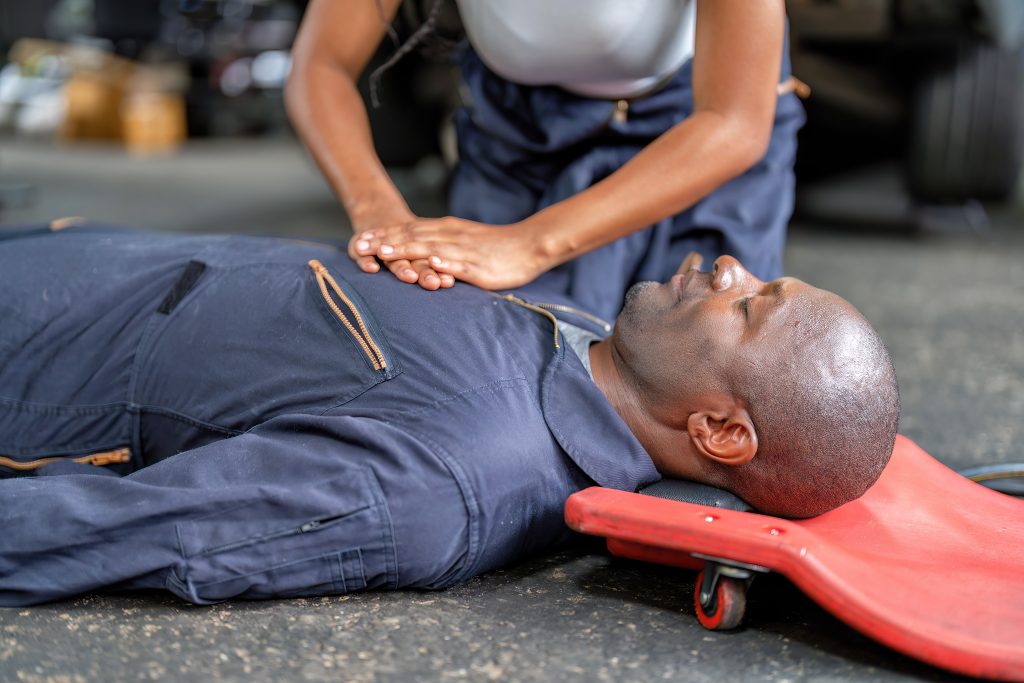
- Adult Compression Technique:
- Use the heel of one hand placed on the center of the chest (lower half of the sternum).
- Place the heel of the second hand on top of the first, interlacing the fingers.
- Keep elbows locked and push straight down, using body weight to achieve the 2-inch minimum depth.
- Child Compression Technique:
- For an average-sized child, use the heel of only one hand.
- For a larger child, or if a single hand cannot achieve the required depth, the rescuer may use the two-hand, interlacing technique (similar to an adult).
- The goal is to use the minimal effective force to reach the 2-inch depth.
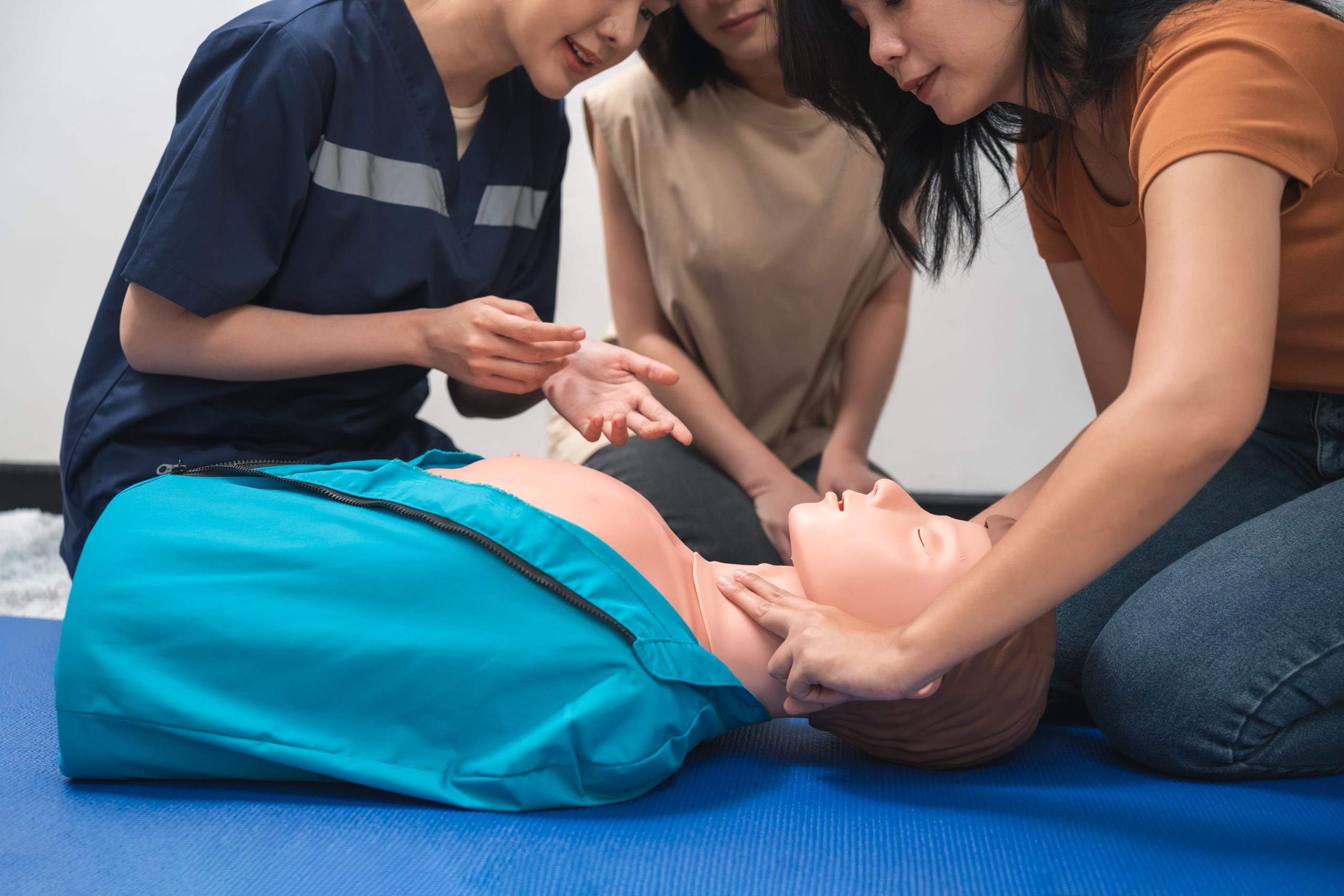
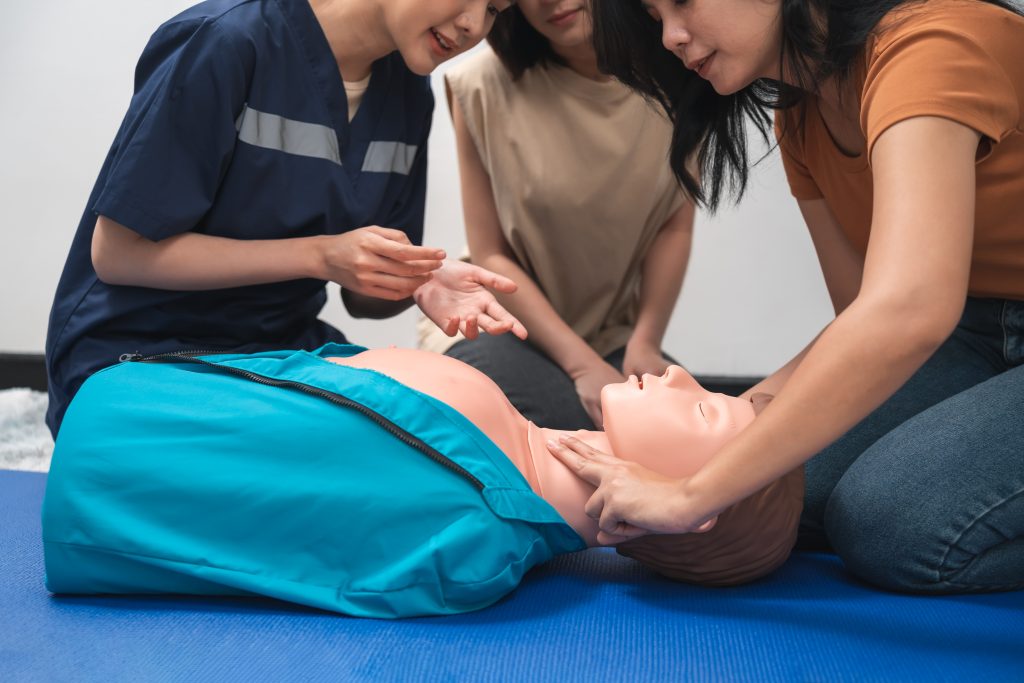
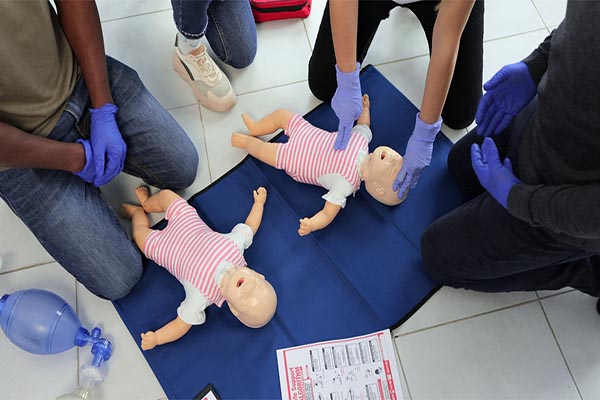
- Infant Compression Technique: This is the most distinct technique, using fingers rather than hands.
- Lone Rescuer: Use the tips of two fingers (index and middle fingers or middle and ring fingers). Place the fingers on the breastbone, just below the imaginary line connecting the nipples.
- Two Rescuers: The two-thumb encircling hands technique is preferred. Rescuers wrap their hands around the infant’s torso and use their two thumbs side-by-side to compress the chest. This method often provides better depth and blood pressure.
Correct placement and technique are non-negotiable for maximizing blood flow while preventing severe, unnecessary injury.
Is the compression rate the same for pediatric and adult victims?
One of the few standardized elements in CPR is the speed at which chest compressions are delivered. This consistency helps maintain a universally acceptable pace for blood circulation, regardless of the victim’s age.
The rate of compressions is designed to mimic a rapid, life-sustaining heartbeat.
- Universal Compression Rate: For adults, children, and infants, the chest compression rate is consistently 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
- This rapid pace ensures continuous and adequate pressure is maintained on the heart.
- Rescuers are encouraged to use a song with the correct tempo, such as “Stayin’ Alive” or “Another One Bites the Dust,” to help maintain a steady rhythm.
The rate is critical, but the compressions must be high-quality, meaning they are delivered at the correct depth with full chest recoil between each push. Pushing too quickly or too slowly diminishes the overall effectiveness of the CPR cycle.
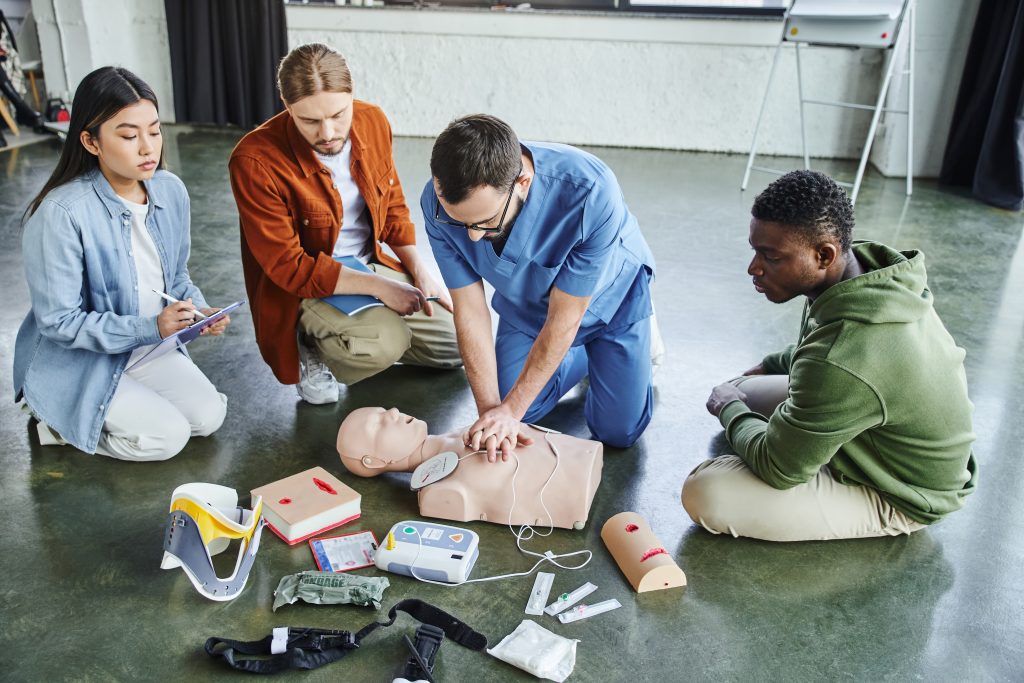

What is the crucial difference in the compression-to-ventilation ratio?
The ratio of compressions to breaths reflects the underlying cause of the arrest and the number of rescuers present. This balance is especially critical in pediatric care, where delivering oxygen is often the main intervention needed.
The C:V ratio varies based on patient age and team composition.
- Adult Compression-to-Ventilation Ratio:
- One or Two Rescuers: The standard ratio is 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths (30:2).
- This universal ratio for adults prioritizes circulation over ventilation, given the likely cardiac cause of the arrest.
- Pediatric (Child and Infant) Compression-to-Ventilation Ratio: This is where the pediatric protocol diverges significantly in two-rescuer scenarios.
- Single Rescuer: The ratio is 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths (30:2). This simplified ratio is used for lay rescuers to minimize confusion and maximize compliance.
- Two or More Rescuers (Healthcare Providers): The ratio shifts to 15 compressions to 2 rescue breaths (15:2). This change reflects the crucial need for more frequent ventilations in a child or infant, whose cardiac arrest is typically caused by oxygen deprivation. A team allows the compressions to be interrupted for breaths more frequently without unduly fatiguing the compressor.
What unique considerations are required for giving rescue breaths to an infant?
While rescue breaths are a component of all standard CPR, the technique used for an infant must be modified to account for their extremely small and delicate airway. Improper technique can lead to serious complications.
Gentleness and a proper seal are paramount when ventilating an infant.
- Airway Position: The infant’s airway should be positioned neutral or slightly past neutral. Over-tilting the head, the standard head-tilt/chin-lift maneuver used on adults, can actually close off an infant’s soft trachea.
- Sealing the Airway: The rescuer must cover both the infant’s mouth and nose with their own mouth to create a complete seal. This dual-seal is necessary because the infant’s face is too small to cover the mouth alone.
- The Breath: The rescuer must deliver a gentle puff of air from their cheeks, not a full lungful. The goal is simply to make the infant’s chest visibly rise, indicating the breath entered the lungs. Forcing too much air too quickly can inflate the stomach, leading to vomiting and aspiration, which further complicates the emergency.
The precision and gentleness of pediatric rescue breaths underscore why hands-on training is so vital for this skill set.
When should an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) be used, and what are the pediatric variations?
An AED is the only definitive treatment for an adult cardiac arrest caused by a lethal electrical rhythm. However, using this powerful device on a small child or infant requires specific modifications to prevent delivering a dangerous electrical dose.
AED usage is a critical bridge to advanced care for all age groups.
- Determining Usage: An AED should be applied as soon as it is available for any victim experiencing sudden, pulseless cardiac arrest.
- The Power Issue (Dose Attenuation):
- Adult AEDs deliver a standard, high-energy electrical shock.
- Pediatric AEDs require attenuator pads (child pads) that reduce the energy level of the shock delivered.
- These specialized pads should be used for children up to age 8 or approximately 55 lbs (25 kg).
- If pediatric pads are unavailable for a child, using adult pads is preferred over delaying defibrillation, though the dose will be higher than recommended. Never use adult pads on an infant if pediatric pads are available.
- Pad Placement:
- Adult and Child: Standard placement is typically anterior-lateral (one pad on the upper right chest, one on the lower left side).
- Infant and Small Child: To prevent the pads from touching (which could short-circuit the shock), anterior-posterior placement is often necessary. One pad is placed on the front of the chest (sternum), and the second pad is placed on the back, between the shoulder blades.
The rule remains consistent: if the AED advises a shock, deliver it without hesitation, provided the correct pediatric equipment is being utilized.
What is the distinction between “Hands-Only CPR” and full CPR for children?
The concept of “Hands-Only CPR” has gained traction globally due to its simplicity and effectiveness for adults. However, this simplified approach is not generally recommended for children and infants, given their underlying physiology.
The utility of Hands-Only CPR changes based on the likely cause of arrest.
- Hands-Only CPR for Adults: Highly recommended for lay rescuers who witness an adult collapse. Since the arrest is likely cardiac, continuous, high-quality compressions are often enough to keep the victim alive for a few minutes. Eliminating the need for rescue breaths encourages more bystanders to act immediately.
- Hands-Only CPR for Children and Infants: This is not the primary recommendation. Since pediatric arrests are typically oxygen-related, rescue breaths are essential. The combination of compressions and ventilations (30:2 or 15:2) must be used. While compressions-only is better than doing nothing, skipping the breaths drastically lowers the survival odds for a child or infant whose body is already starved of oxygen.
Therefore, for anyone caring for children, mastering the proper technique for rescue breaths is just as vital as mastering chest compressions.
How does the goal of resuscitation differ in pediatrics compared to adults?
While the ultimate goal of all resuscitation efforts is to restore life, the immediate physiological goal shifts significantly based on age. In adults, the immediate focus is restoring circulation to a heart that has suddenly failed. In pediatrics, the focus is broader and often starts earlier in the sequence of intervention.
The approach is tailored to the patient’s primary vulnerability.
- Adult Goal: Quickly treat the electrical problem and restart the pump. The heart stopped first, and the rest of the body followed. Rescuers need to prioritize the AED and hard, fast compressions to keep blood flowing.
- Pediatric Goal: Reverse the effects of hypoxia (oxygen deprivation) and prevent circulatory collapse. For children and infants, the respiratory system fails first, and the heart only stops as a secondary event due to lack of oxygen. Therefore, the goal is to aggressively oxygenate the patient (via rescue breaths) while maintaining circulation (via compressions) to prevent the full cardiac arrest from occurring.
This fundamental difference is why pediatric training emphasizes intervening much earlier for severe breathing difficulties before the patient becomes pulseless.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Fear and Action
The world of resuscitation, while governed by universal principles of circulation and oxygenation, demands a nuanced and adaptable approach based on the size and age of the victim. From the critical differences in compression depth (1.5 inches for an infant versus 2 inches for a child and 2+ inches for an adult) to the strategic use of C:V ratios (15:2 for a two-rescuer pediatric team), these distinctions are life-saving. Knowing the right response, whether to Call First or Care First, is the difference between an optimal outcome and a tragic delay.
The ability to look at a small victim and immediately know to shift from two hands to two fingers, or to prioritize breaths over compressions, is a skill that must be practiced until it becomes muscle memory. CPR certification is not just a requirement; it is a profound commitment to readiness. By mastering the pediatric and adult protocols, you are prepared to act effectively in any emergency scenario, protecting your loved ones, colleagues, and community members, regardless of their size.
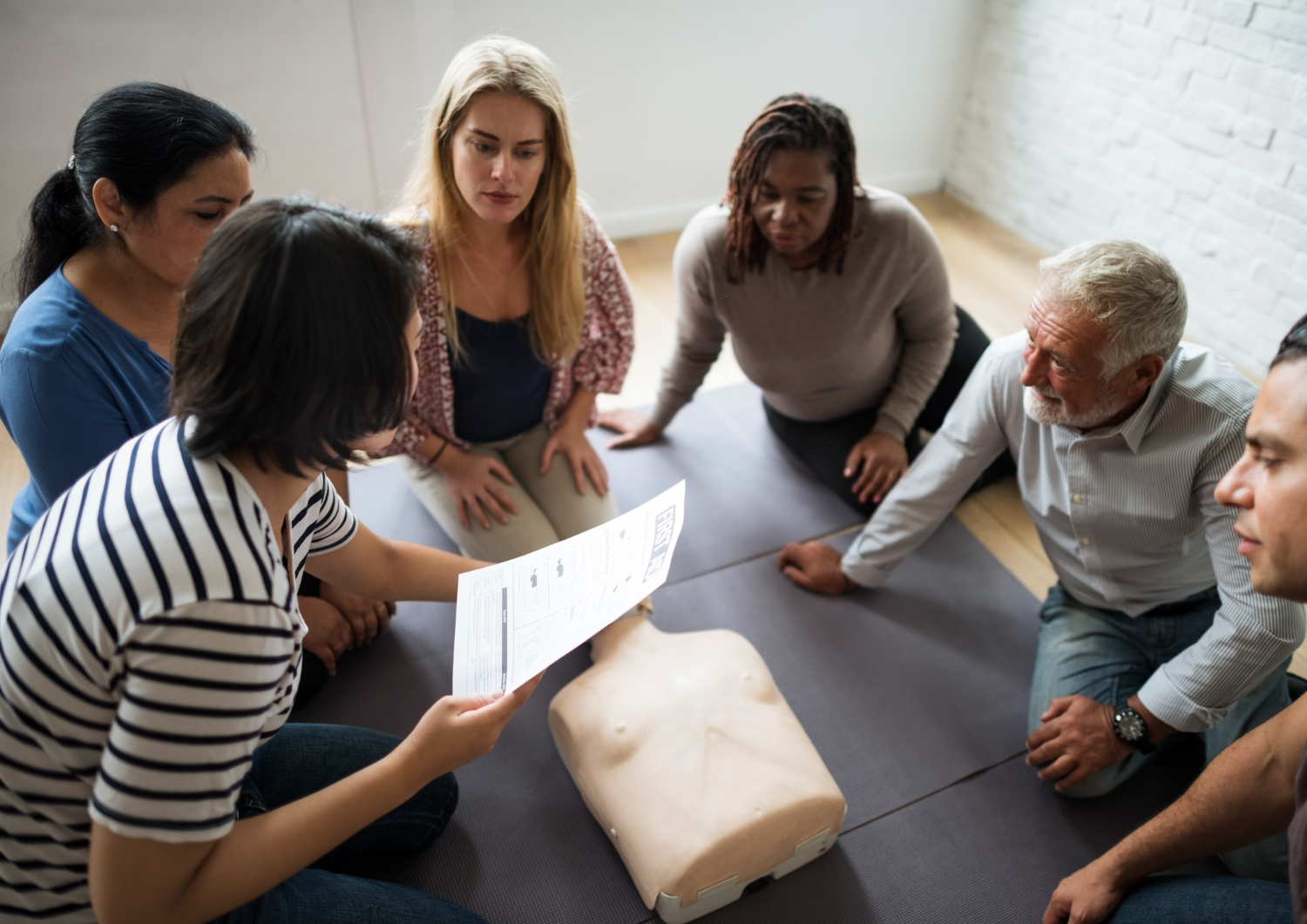
The best way to solidify this knowledge is through hands-on practice with certified instructors.
Take the next step and transform knowledge into life-saving ability.
Ready to master these life-saving skills? CPR Classes Near Me Baltimore is an American Heart Association Certified Training Site offering the highest quality BLS CPR and AED certification courses. Our expert instructors provide the hands-on practice needed to confidently perform resuscitation on victims of all ages, from infants to adults.
- Receive your official AHA BLS eCard the same day you complete the class.
- Learn all the critical differences between adult and pediatric CPR techniques.
- Book Your Life-Saving Course Today!
Contact CPR Classes Near Me Baltimore to secure your spot in an upcoming class and be prepared to save a life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pediatric vs. Adult CPR
What is the most critical difference between pediatric and adult CPR?
The most critical difference is the primary cause of the emergency and the resulting priority of care. For adults, the cardiac arrest is usually a primary electrical or heart-related problem, prioritizing immediate, high-quality chest compressions to circulate remaining oxygen. For infants and children, the arrest is most often secondary to respiratory failure (a lack of oxygen), making rescue breaths equally, if not more, critical in the initial stages to re-oxygenate the victim. This physiological difference dictates the variations in compression-to-ventilation ratios and the timing of calling for help.
If I am a single rescuer, should I use the 30:2 or 15:2 ratio for a child?
As a single rescuer, you should use the 30 compressions to 2 rescue breaths (30:2) ratio for both children and infants. The 30:2 ratio is standardized for lay rescuers of all age groups to simplify training and memory recall during high-stress, single-person emergencies. The 15 compressions to 2 rescue breaths (15:2) ratio is primarily reserved for two or more trained healthcare providers working together on a child or infant, as it allows for more frequent oxygen delivery while minimizing rescuer fatigue.
Can I use the two-thumb technique for infant compressions if I am alone?
While the two-thumb encircling hands technique is highly effective and recommended for two-rescuer infant CPR, a lone rescuer should use the two-finger technique. The two-finger method allows the rescuer to quickly transition between compressions and rescue breaths (30:2) without having to move their entire body position around the infant. The two-thumb technique requires the rescuer to be positioned near the infant’s feet, making the transition to the head for ventilation awkward and time-consuming, leading to critical delays in blood flow and oxygen delivery.
How do I know when a child is old enough to be treated as an adult in CPR?
A victim is considered an adult for the purposes of CPR when they show signs of puberty. This is the definitive anatomical marker, regardless of their chronological age. For females, signs of puberty include breast development; for males, it includes the presence of axillary (underarm) hair. If the victim has already reached these stages of physical maturity (e.g., breast development in females, axillary hair in males), the rescuer should use the standard adult protocol. If you are uncertain or the child is particularly large but not yet showing signs of puberty, it is reasonable to use the child protocol with a two-hand technique to ensure adequate depth.
What is the most common injury caused by performing pediatric CPR incorrectly?
The most common severe injury from incorrectly performed CPR on children and infants is a rib fracture or sternal injury, often resulting from excessive force or improper hand placement. Over-compressing the chest, which occurs when a rescuer uses too much force (applying adult-level pressure) or fails to place their hands correctly, is the leading cause. It is why guidelines emphasize compressing to only about one-third the depth of the chest, and using only one hand or two fingers/thumbs for children and infants, respectively.