CPR: Comprehensive Emergency Preparedness for Home Health Aides
CPR: Comprehensive Emergency Preparedness for Home Health Aides

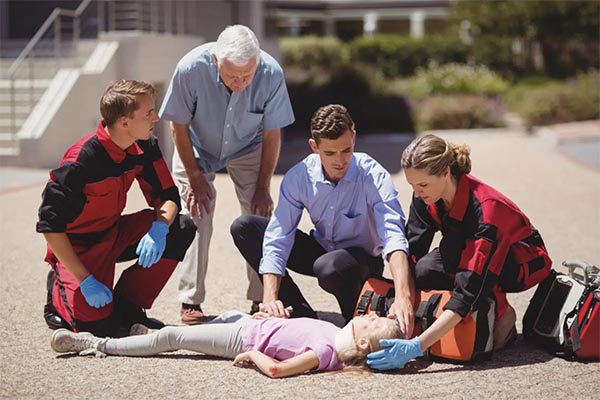
In the field of home healthcare, emergencies can arise at any moment. As a home health aide, being prepared for emergencies goes beyond just knowing CPR. It involves understanding various aspects of emergency preparedness to ensure the safety and well-being of the clients you serve. This guide will delve into the essential components of emergency preparedness for home health aides, providing you with the knowledge and confidence to handle any situation.
Understanding CPR Readiness
The Basics of CPR
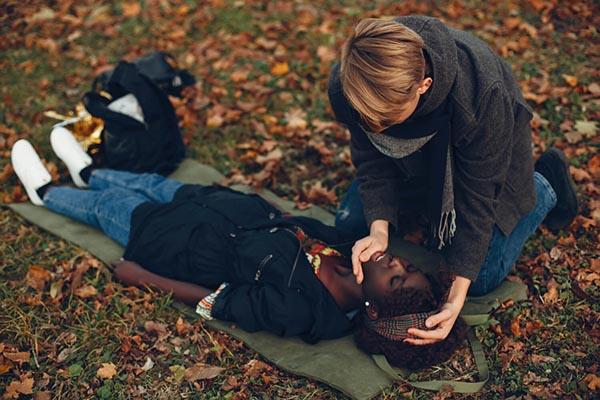
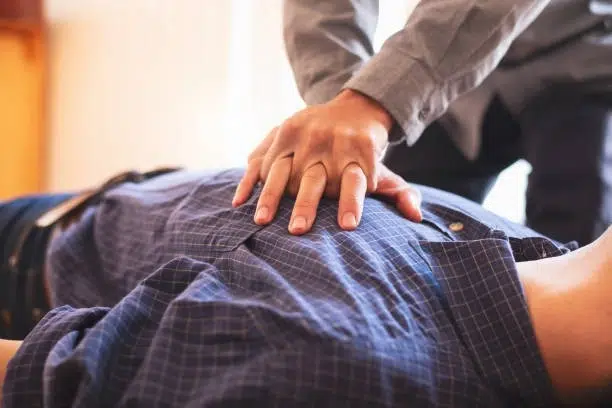
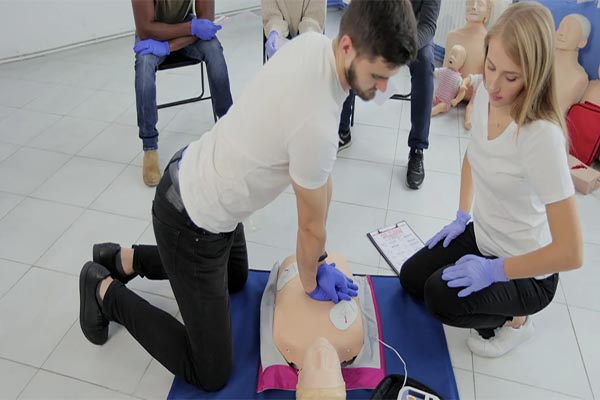
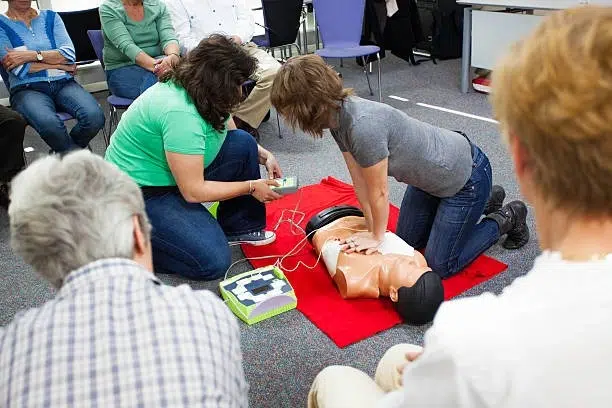
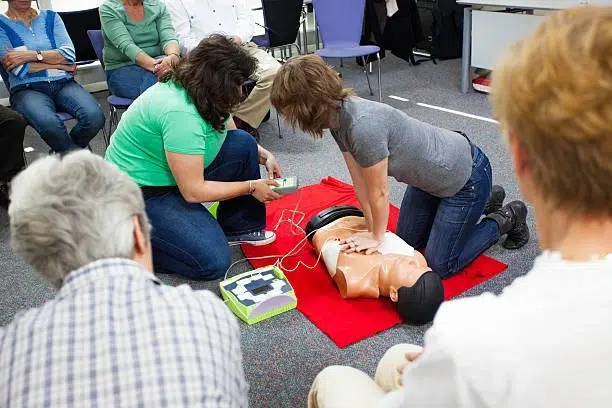
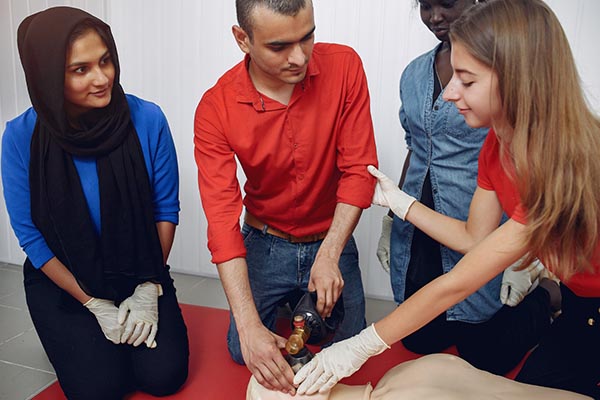
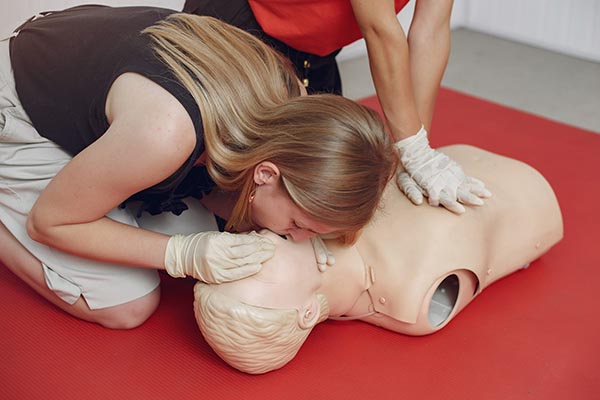
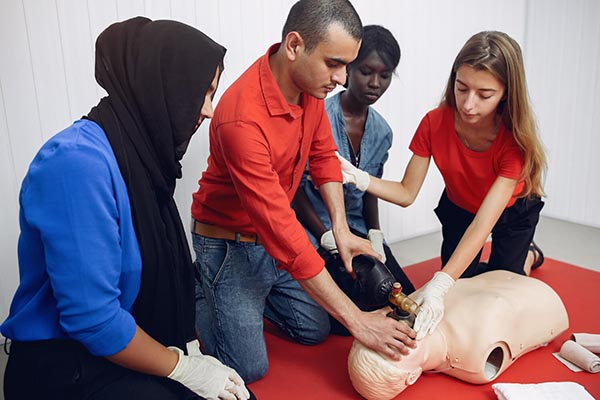
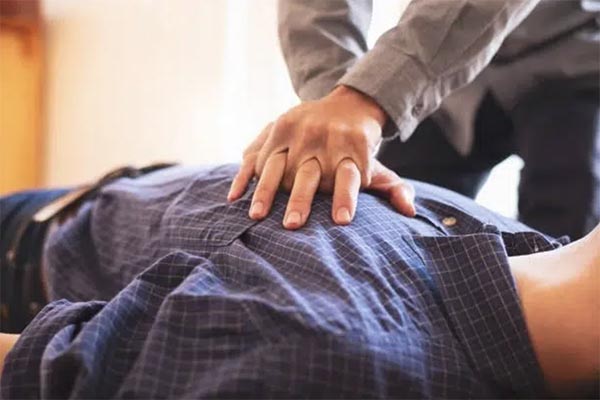
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a critical life-saving technique that all home health aides should master. It is used to maintain blood flow to the brain and heart in emergencies like cardiac arrest. While CPR is fundamental, it is just one part of a comprehensive emergency response plan.

Regular CPR Certification
Staying current with your CPR certification is crucial. Most certifications require renewal every two years. Regular training ensures you are up-to-date with the latest techniques and guidelines, boosting your confidence and effectiveness in emergencies.
Developing an Emergency Response Guide
Identifying Potential Emergencies
Emergencies in home healthcare can range from medical crises, such as heart attacks or strokes, to environmental dangers like fires or severe weather. Understanding the types of emergencies you might encounter helps in preparing appropriate response plans.
Creating a Customized Emergency Plan
Every client has unique needs and risks. Work with your client and their family to develop a personalized emergency response plan. This plan should include emergency contact information, preferred hospitals, and any specific medical instructions or needs.
Assembling an Emergency Kit
An emergency kit is a vital component of preparedness. It should include basic medical supplies, personal protective equipment (PPE), a flashlight, batteries, non-perishable food, water, and any specific medications or equipment your client may need. Regularly check and update the kit to ensure everything is in working order and not expired.
Training for Various Emergency Scenarios
Medical Emergencies
- Heart Attack: Recognize the signs, such as chest pain or discomfort, and act quickly by calling emergency services and providing CPR if necessary.
- Stroke: Be aware of the FAST (Face, Arms, Speech, Time) approach to identify stroke symptoms and act swiftly to get medical help.
- Seizures: Ensure the person’s safety during a seizure by clearing the area of sharp objects and placing them in a recovery position once the seizure ends.
Environmental Emergencies
- Fire: Know the exit routes, how to use a fire extinguisher, and practice fire drills with your client.
- Severe Weather: Understand the local hazards, such as tornadoes or hurricanes, and have a plan for sheltering in place or evacuating if needed.
Violence or Intruder Situations
- Ensure that your client’s home is secure and know how to contact the authorities quickly.
- Develop a code word or phrase with your client to signal distress without alerting an intruder.
Communication is Key
Keeping Lines Open
Communication is crucial during emergencies. Ensure you have a reliable means of communication, whether it’s a mobile phone or a landline, and know the emergency numbers in your area.
Coordinating with Healthcare Providers
Maintain a list of your client’s healthcare providers and keep them informed about any changes in the client’s condition or emergency plans. This coordination ensures that everyone involved in the client’s care is on the same page.
Psychological Preparedness
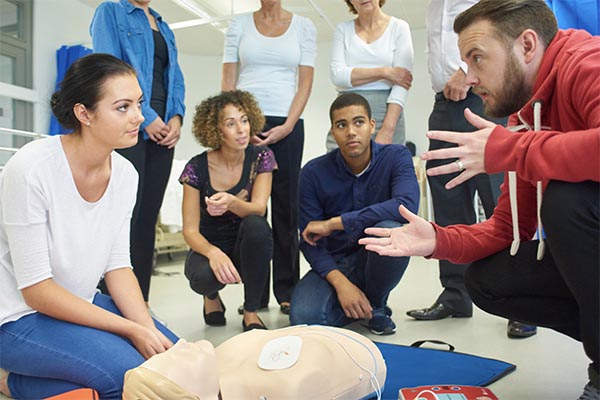

Managing Stress and Anxiety
Emergencies can be stressful and overwhelming. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness to maintain calm and focus during crises.
Providing Emotional Support
Your role extends to offering emotional support to your client during and after an emergency. Reassure them, keep them informed, and involve them in decision-making to help reduce their anxiety.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Attending Workshops and Training
Participate in workshops and training sessions focused on emergency preparedness. These can provide valuable insights and practical skills that enhance your readiness.
Evaluating and Updating Emergency Plans
After any emergency, review what happened, what worked, and what didn’t. Use this evaluation to update and improve your emergency plans and procedures.
Staying Informed About Latest Guidelines
Keep abreast of the latest guidelines and recommendations from reputable sources like the American Heart Association or the Red Cross. This ensures that your knowledge and skills are current and effective.
Conclusion
Being a home health aide means being prepared to handle any emergency with skill and confidence. By going beyond CPR and embracing a comprehensive approach to emergency preparedness, you can ensure the safety and well-being of your clients. Remember, preparedness is an ongoing process that involves planning, training, communication, and continuous improvement. Equip yourself with these tools, and you will be ready to face any challenge that comes your way.
Take the Next Step in Preparedness
Now that you understand the importance of being prepared for emergencies, it’s time to take action. Ensure you are ready to handle any situation by obtaining your CPR certification. Visit CPR Classes Near Me to find a class in your area. These classes provide hands-on training from certified professionals, equipping you with the skills and confidence needed to respond effectively in critical situations. Don’t wait—register today and take a crucial step in enhancing your emergency preparedness skills.
AHA BLS CPR & AED Classes
FAQ
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!
Recent Posts
- How to Create a Workplace First Aid Plan That Saves Lives
- Why Pair CPR Certification with First Aid Training: The Complete Safety Combo
- Tips to Pass Your CPR Certification Test the First Time
- Hospitality Staff: Why CPR Training Is a Must-Have
- The Importance of CPR and AED Training for Flight Attendants