CPR for Professionals in Colorado Springs: Fulfilling Workplace Safety Requirements

CPR for Professionals in Colorado Springs: Fulfilling Workplace Safety Requirements

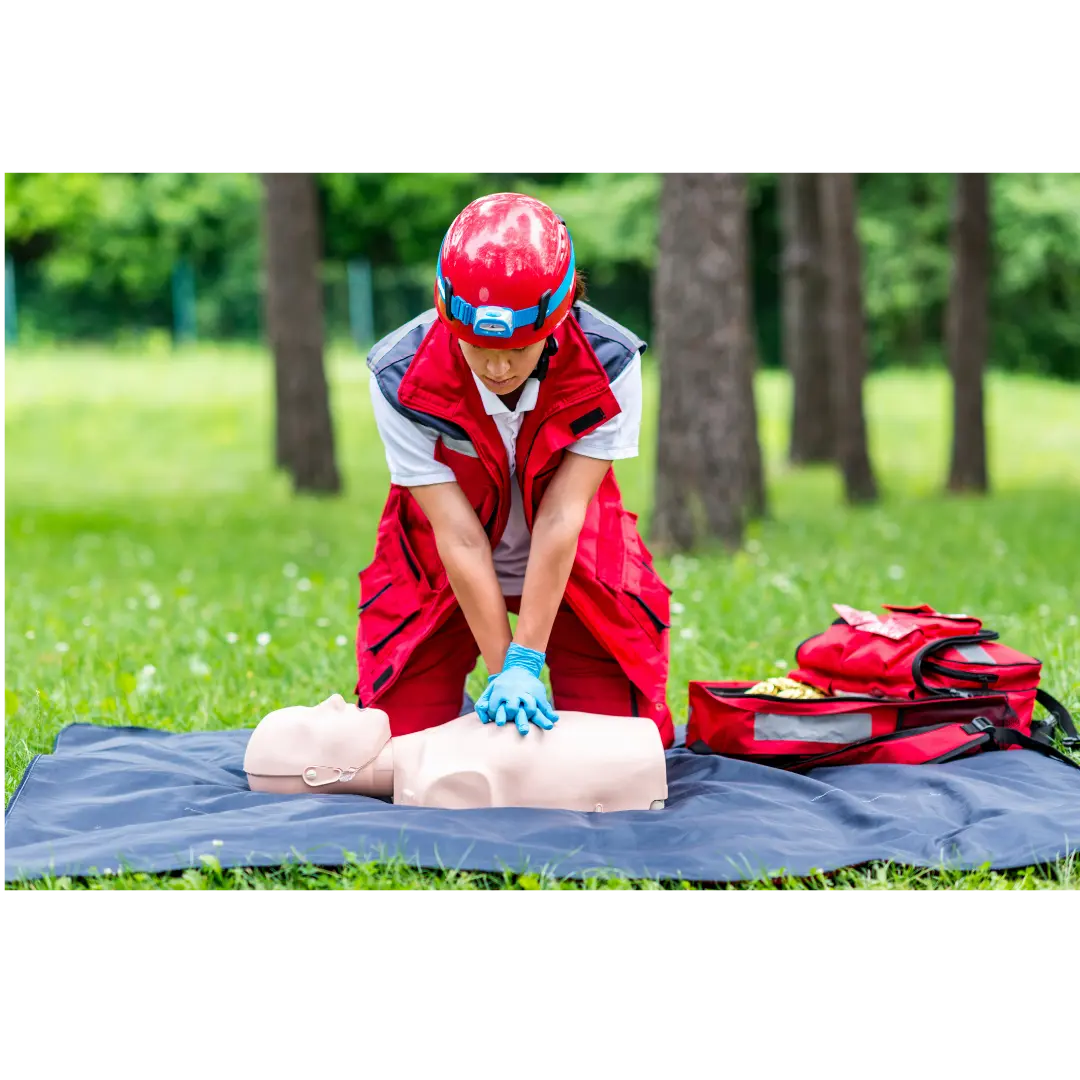
In today’s fast-paced world, workplace safety is paramount. Every employer has a responsibility to ensure a safe environment for their employees. One crucial aspect of workplace safety involves equipping employees with the skills to respond to emergencies, particularly medical emergencies. Equipping your staff with CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) certification is an investment in the well-being of your employees and demonstrates your commitment to a safe work environment. This article explores the importance of CPR for Professionals in Colorado Springs, its role in fulfilling workplace safety requirements, and resources for obtaining CPR certification in the city.
Why CPR Certification is Crucial for Professionals in Colorado Springs?
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a leading cause of death in the United States, claiming hundreds of thousands of lives each year. It can strike anyone, anywhere, at any time. The critical minutes following an SCA are crucial for survival. Early intervention with CPR significantly increases the chances of survival.
Here’s why CPR certification is essential for professionals in Colorado Springs:
- Increased Survival Rates: Studies have shown that immediate CPR, administered within the first few minutes of SCA, can double or triple the victim’s chance of survival.
- Reduced Brain Damage: When the heart stops pumping blood, oxygen delivery to the brain ceases. Prompt CPR helps maintain some circulation, minimizing brain damage and improving the chances of a full recovery.
- Improved Employee Confidence: CPR certification empowers employees to act decisively in emergencies. Knowing how to perform CPR can provide a sense of control and confidence in a stressful situation.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety Culture: When a significant number of employees are CPR-certified, it fosters a culture of safety and preparedness within the workplace. This can have a positive impact on employee morale and overall well-being.
- Fulfilling Workplace Safety Requirements: OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) doesn’t mandate CPR certification for all workplaces. However, some industries and specific job roles may have CPR training as a requirement.
Does Colorado Law Require CPR Certification for Professionals?
Currently, there is no state law in Colorado mandating CPR certification for all workplaces. However, specific industries or professions may have regulations requiring CPR training for their employees. It’s crucial for employers to consult with the relevant regulatory bodies governing their industry to determine any specific CPR training requirements. Even in the absence of legal mandates, CPR certification demonstrates an employer’s proactive approach to workplace safety and could be considered a best practice.
Here are some resources to help you determine if CPR certification is required for your industry in Colorado:
- Colorado Department of Labor and Employment
- OSHA Colorado State Plan
Benefits of CPR Certification for Colorado Spring Businesses
Beyond the potential legal requirements and the ethical imperative of employee safety, CPR certification offers several benefits for Colorado Spring businesses:
- Reduced Costs: The cost of CPR training is minimal compared to the potential financial and human cost of a workplace emergency. Early intervention with CPR can prevent fatalities, minimizing associated medical expenses, worker’s compensation claims, and lost productivity.
- Improved Public Image: Demonstrating a commitment to employee safety through CPR training enhances a company’s public image. Potential customers and employees are more likely to be drawn to organizations prioritizing employee well-being.
- Increased Employee Morale: Equipping employees with potentially lifesaving skills fosters trust and a sense of security within the workplace. Employees feel valued and appreciate the investment made in their safety, leading to increased morale and loyalty.
Finding the Right CPR Certification Course for Professionals in Colorado Springs
Colorado Springs offers a variety of CPR training providers. When choosing a CPR course for your employees, consider the following factors:
- Certification Type: There are various CPR certification types available. The most common courses for professional settings are Basic Life Support (BLS) for Healthcare Providers and American Red Cross CPR/AED for the Professional Rescuer/Provider. Choosing the appropriate certification depends on job responsibilities and potential risks within the workplace.
- Instructor Qualifications: Ensure instructors are certified by a reputable organization like the American Heart Association (AHA) or the American Red Cross. Experienced trainers can provide in-depth knowledge and hands-on practice opportunities.
- Course Format: CPR training is offered in various formats, including traditional classroom settings, blended learning (combining online modules with hands-on practice), and private on-site training. Consider the learning preferences and time constraints of your employees when choosing a format.
- Cost: Costs for CPR training can vary depending on the course type, duration, and provider. Compare pricing and offerings from different providers to find the best fit for you.
- Renewal Requirements: CPR certification typically requires renewal every two years. Choose a provider offering renewal courses for your employees’ convenience.
- Additional Training Options: Some providers might offer additional training options beyond basic CPR, such as using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) or CPR for infants and children. Consider incorporating these options if relevant to your workplace environment.
Expanding Your Search for CPR Certification Courses in Colorado Springs
Identifying the right CPR training provider for your employees in Colorado Springs requires exploring various resources. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the options mentioned previously, along with additional suggestions to broaden your search:
- American Heart Association (AHA) Training Locator: This online tool allows you to search for AHA-authorized CPR training providers in your area by entering your zip code or city name. The locator provides detailed information about each provider, including contact details, course offerings, and class schedules. This is a valuable resource for finding reputable training centers that adhere to the latest AHA guidelines for CPR and AED use.
- American Red Cross CPR Courses: The American Red Cross is another prominent organization offering CPR certification courses across the United States. Their website allows you to browse CPR training options specifically designed for professional rescuers and providers. Consider the course descriptions, schedules, and pricing to determine if the Red Cross offerings align with your needs. In addition to the main website, you can also visit the local Red Cross chapter serving Colorado Springs for more information on their CPR training programs and potential registration options.
Colorado Springs Chamber of Commerce: The Colorado Springs Chamber of Commerce is a membership organization dedicated to supporting businesses in the area. While they might not maintain a dedicated list of CPR training providers, the Chamber can be a valuable resource for connecting with local businesses.
The CPR Certification Process for Professionals in Colorado Springs
Equipping your employees with CPR certification in Colorado Springs involves a well-defined process. Let’s delve deeper into each step to ensure a smooth and successful experience for both you and your staff:
1. Choosing a Training Provider
As mentioned earlier, explore the resources provided to identify reputable CPR training providers in Colorado Springs. Here are some additional factors to consider when making your selection:
- Course Options: Review the specific CPR courses offered by each provider. Look for courses designed for professionals, such as Basic Life Support (BLS) for Healthcare Providers, which cater to the needs of professional rescuers in a workplace setting. Some providers might offer additional training options like using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) or CPR for specific age groups. Choose a provider with offerings that align with the potential risks and needs in your workplace.
- Instructor Qualifications: Ensure the instructors are certified by a recognized organization like the American Heart Association (AHA) or the American Red Cross. Experienced trainers can not only impart essential knowledge but also provide valuable insights and practical tips for real-world scenarios. Don’t hesitate to inquire about the instructors’ backgrounds and experience before finalizing your selection.
- Course Format: CPR training is offered in various formats to cater to different learning styles and scheduling needs. Consider the following options:
- Traditional Classroom Setting: This offers a structured learning environment with face-to-face interaction with the instructor and other participants.
- Blended Learning: This combines online modules with in-person skills practice sessions. Online modules allow for a flexible learning pace, while hands-on sessions ensure practical skill development.
- Private On-Site Training: This option provides training at your workplace, minimizing disruption to your normal business operations. It can be particularly beneficial for larger groups of employees.
- Cost and Payment Options: Compare pricing offered by different providers. Some factors influencing cost might include course duration, format, and additional training modules. Inquire about group discounts or payment plans if applicable.
2. Course Registration: Streamlined Sign-Ups
Once you’ve chosen a training provider, proceed with registering your employees for the chosen CPR course. Many providers offer convenient online registration options. During registration, gather necessary employee information such as names, contact details, and any relevant medical history that might impact participation in CPR training. Some providers might require participants to complete online waivers or pre-enrollment modules before attending the hands-on training session.
3. Pre-Coursework: Laying the Foundation
While not all CPR courses in Colorado Springs require pre-coursework, some might involve online modules or readings to introduce participants to basic CPR concepts and procedures. Encourage your employees to complete these pre-course materials diligently. Familiarity with the fundamentals can enhance their learning experience during the hands-on training session.
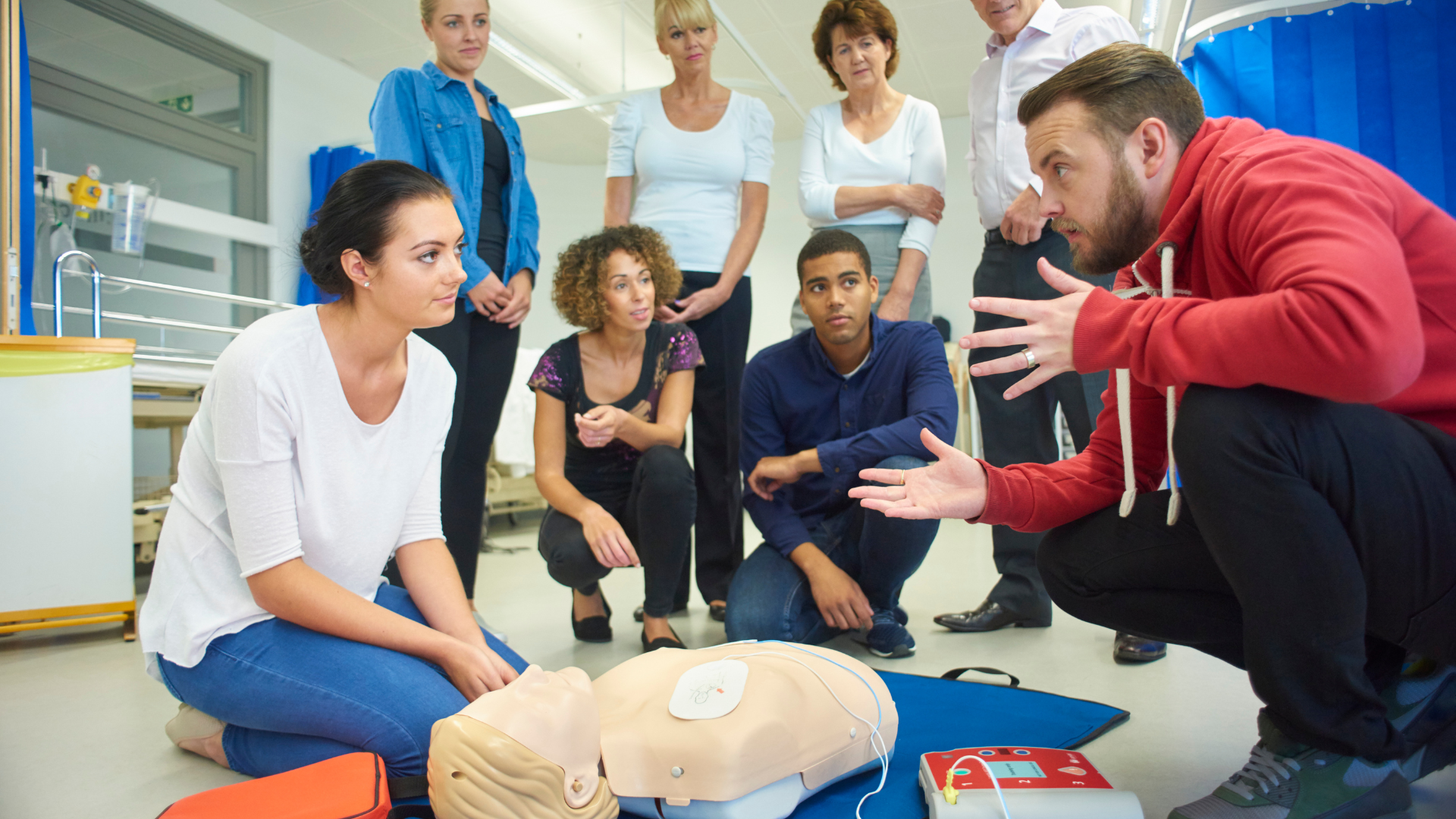
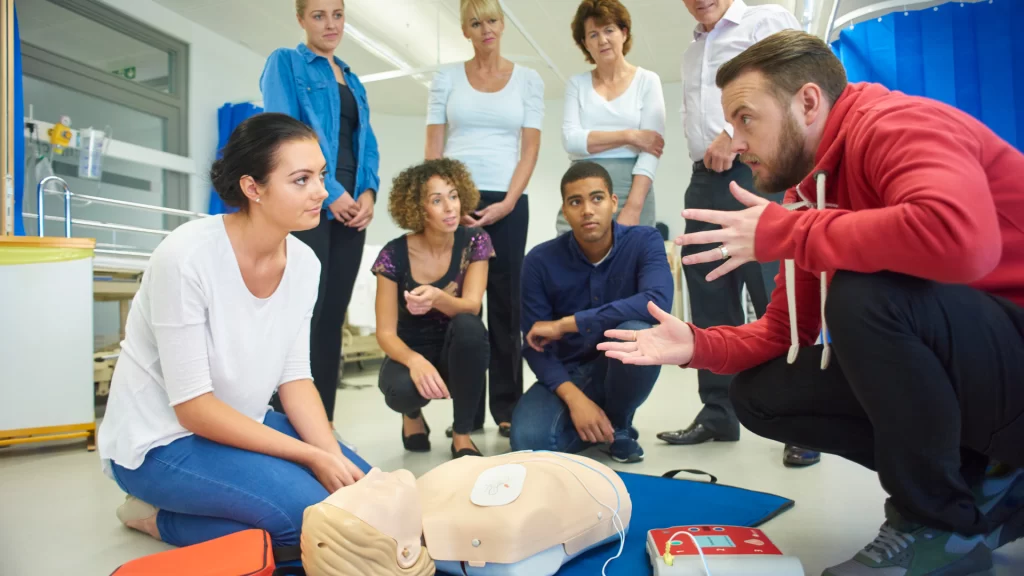
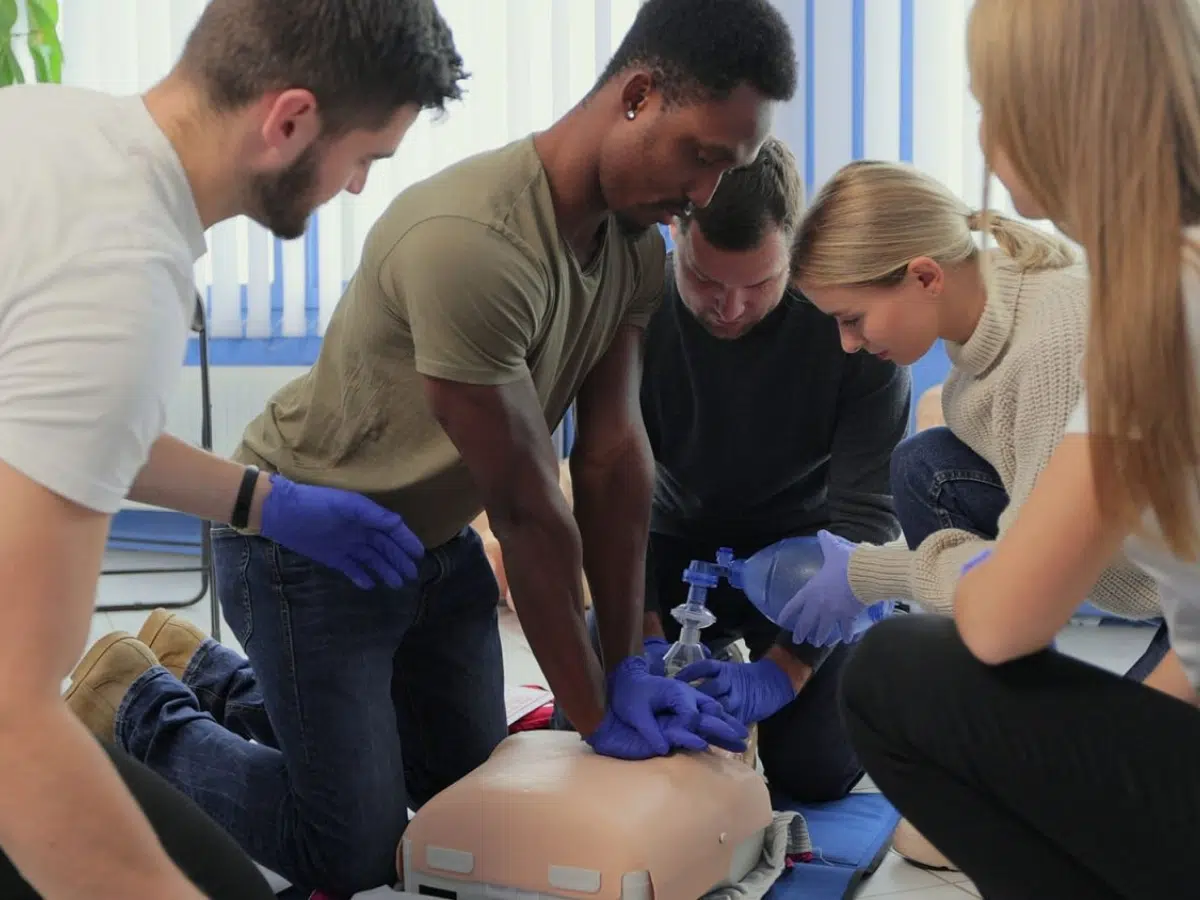
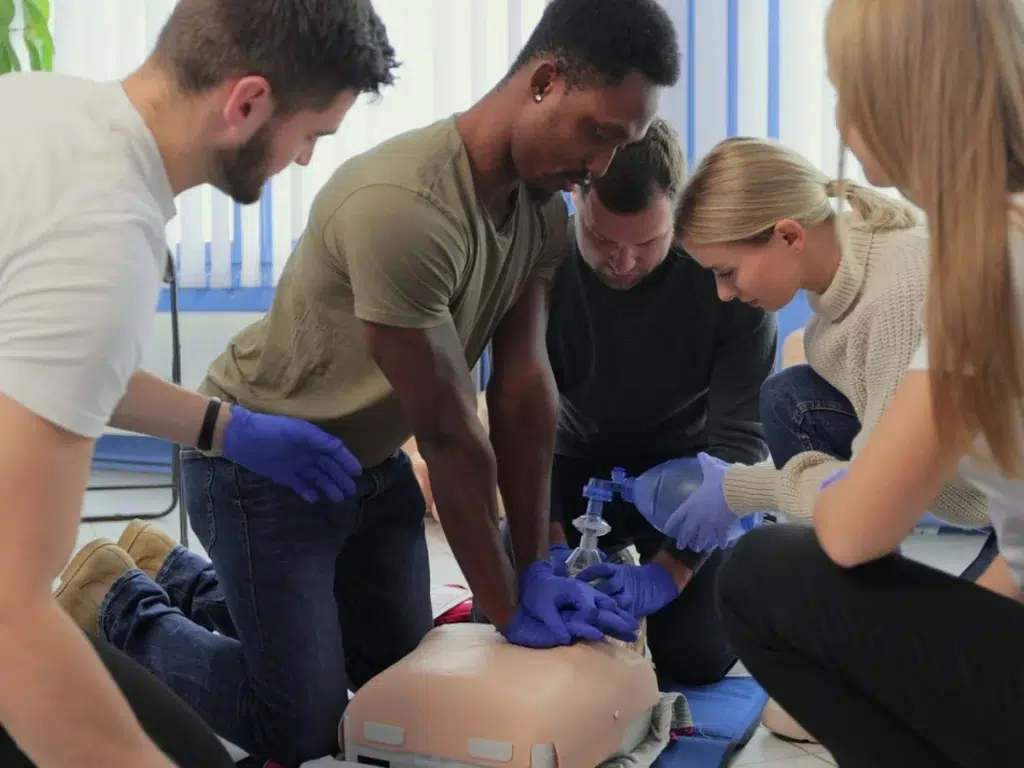
4. Hands-on Training: The Core of Competency
The hands-on training session forms the heart of the CPR certification process. Experienced instructors will guide participants through the various CPR techniques for adults, children, and infants (if applicable to your chosen course). The session will involve:
- Demonstrations: Instructors will clearly demonstrate each CPR technique, including chest compressions, rescue breaths, and AED use.
- Practice Sessions: Participants will have ample opportunities to practice CPR skills on mannequins under the instructor’s supervision. This allows for muscle memory development and ensures proper technique execution.
- Scenario-Based Training: Some courses might incorporate scenario-based training where participants practice CPR procedures in simulated emergency situations. This helps them apply their skills in a more realistic setting and build confidence in their ability to respond effectively in real-world emergencies.
By actively participating in these elements, your employees will gain the necessary knowledge and practical skills to perform CPR confidently.
5. Skills Evaluation: Putting Knowledge into Action
Most CPR courses culminate in a skills evaluation. During this assessment, participants will demonstrate their competence in performing CPR procedures on mannequins. The evaluation might involve individual assessments or simulated scenarios where participants work together as a team. This ensures that participants can effectively perform CPR in various situations.
6. Certification: Recognition of Achievement
Upon successful completion of the course and skills evaluation, participants will receive a CPR certification card. This card typically remains valid for two years, signifying their competency in CPR skills.
Maintaining CPR Certification for Professionals in Colorado Springs
CPR certification requires renewal every two years to ensure continued competency. Many CPR training providers offer renewal courses specifically designed to refresh skills and knowledge. Renewal courses typically involve shorter durations and focus on practical skill demonstrations rather than extensive re-teaching of core concepts.
Here are some tips for maintaining CPR certification for your employees:
- Develop a Renewal Schedule: Establish a system to track employee CPR expiration dates and proactively schedule renewal courses before certifications lapse.
- Utilize Training Reminders: Many training providers offer reminder services to notify employers or employees about upcoming expiration dates.
- Explore Group Renewal Options: Consider enrolling multiple employees in renewal courses together to potentially benefit from discounted group rates.
Conclusion
CPR certification for professionals in Colorado Springs is a valuable investment in workplace safety. It empowers employees to act decisively in emergencies, potentially saving lives. Furthermore, CPR training demonstrates a company’s commitment to employee well-being and fosters a positive safety culture within the workplace. By choosing the right training program and maintaining CPR certifications, Colorado Springs businesses can create a safer environment for their employees and contribute to a more prepared and empowered workforce.