Mastering BLS for Different Age Groups: Adults, Infants, and Children

Mastering BLS for Different Age Groups: Adults, Infants, and Children

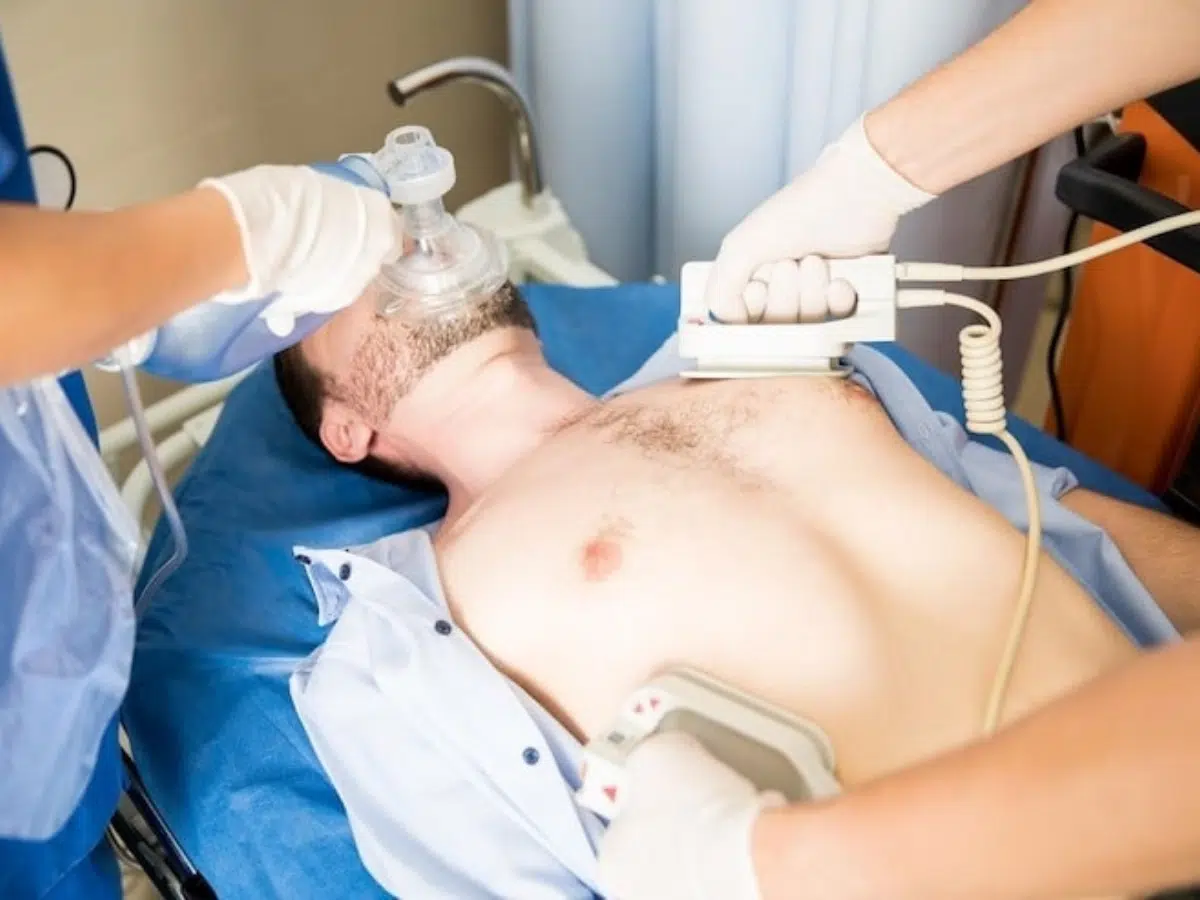
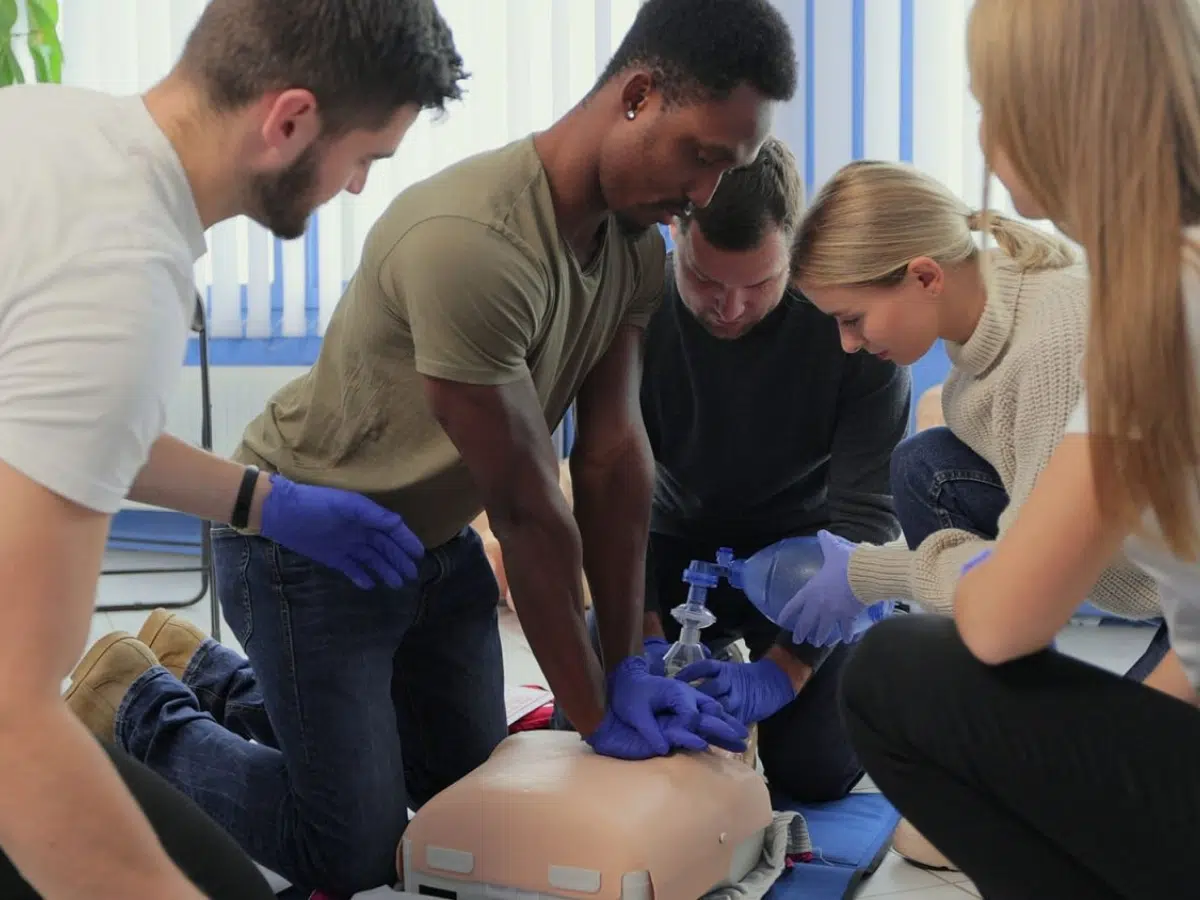
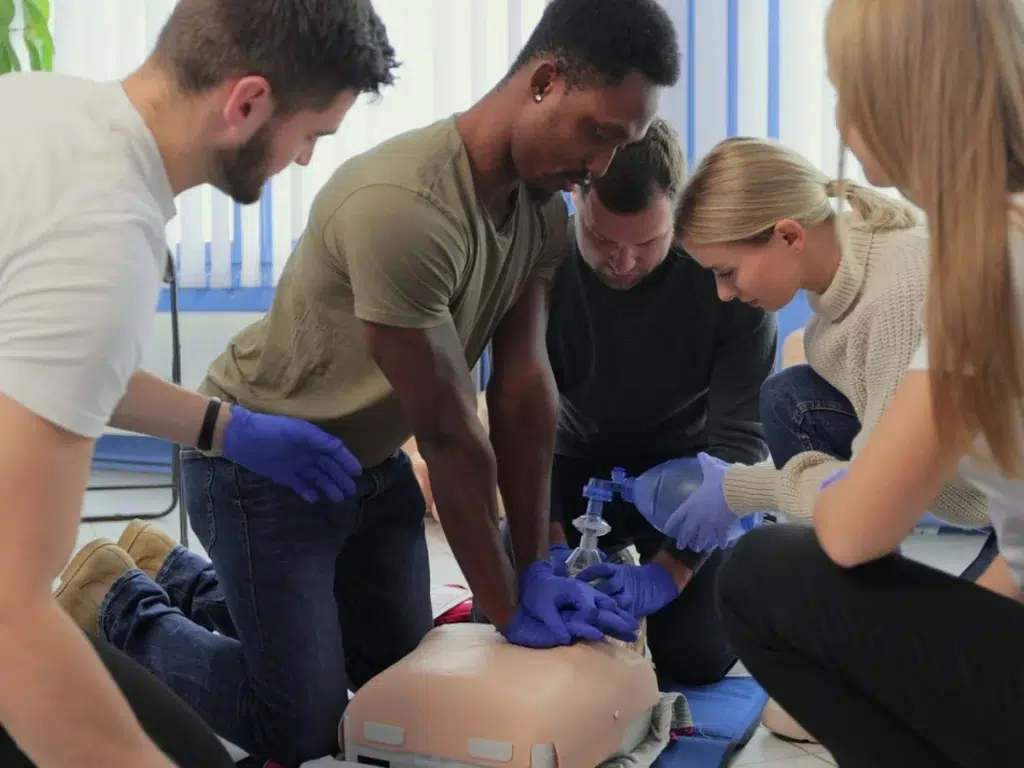
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a fundamental set of life-saving techniques that can be the difference between life and death in emergency situations. Knowing how to administer BLS appropriately to individuals of different age groups is crucial for any first responder, healthcare professional, or even a concerned citizen. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of BLS for adults, infants, and children, providing invaluable insights and tips to empower you to act effectively in critical moments.
BLS for Adults: Key Techniques and Considerations
Recognizing Cardiac Arrest
- When dealing with adults, recognizing signs of cardiac arrest is dominant.
- Look for the absence of breathing or abnormal breathing patterns, unresponsiveness, and the lack of a pulse.
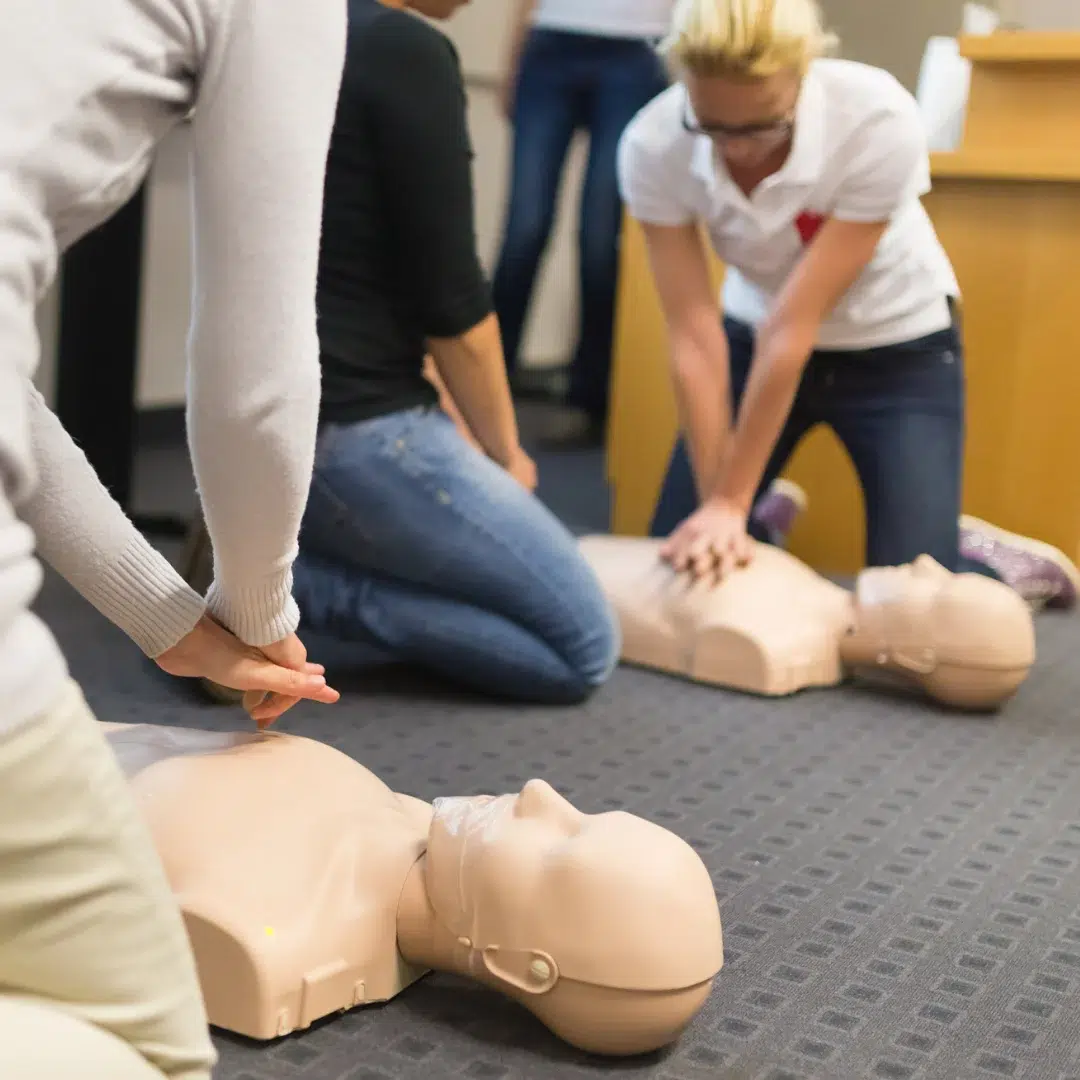
Chest Compressions
- Effective chest compressions are the cornerstone of BLS for adults.
- Administer compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 per minute, allowing for full chest recoil between each compression.
Rescue Breaths
- Proper rescue breathing technique is crucial in adult BLS.
- Ensure the airway is clear and open before delivering rescue breaths, maintaining a ratio of 30 compressions to 2 breaths.
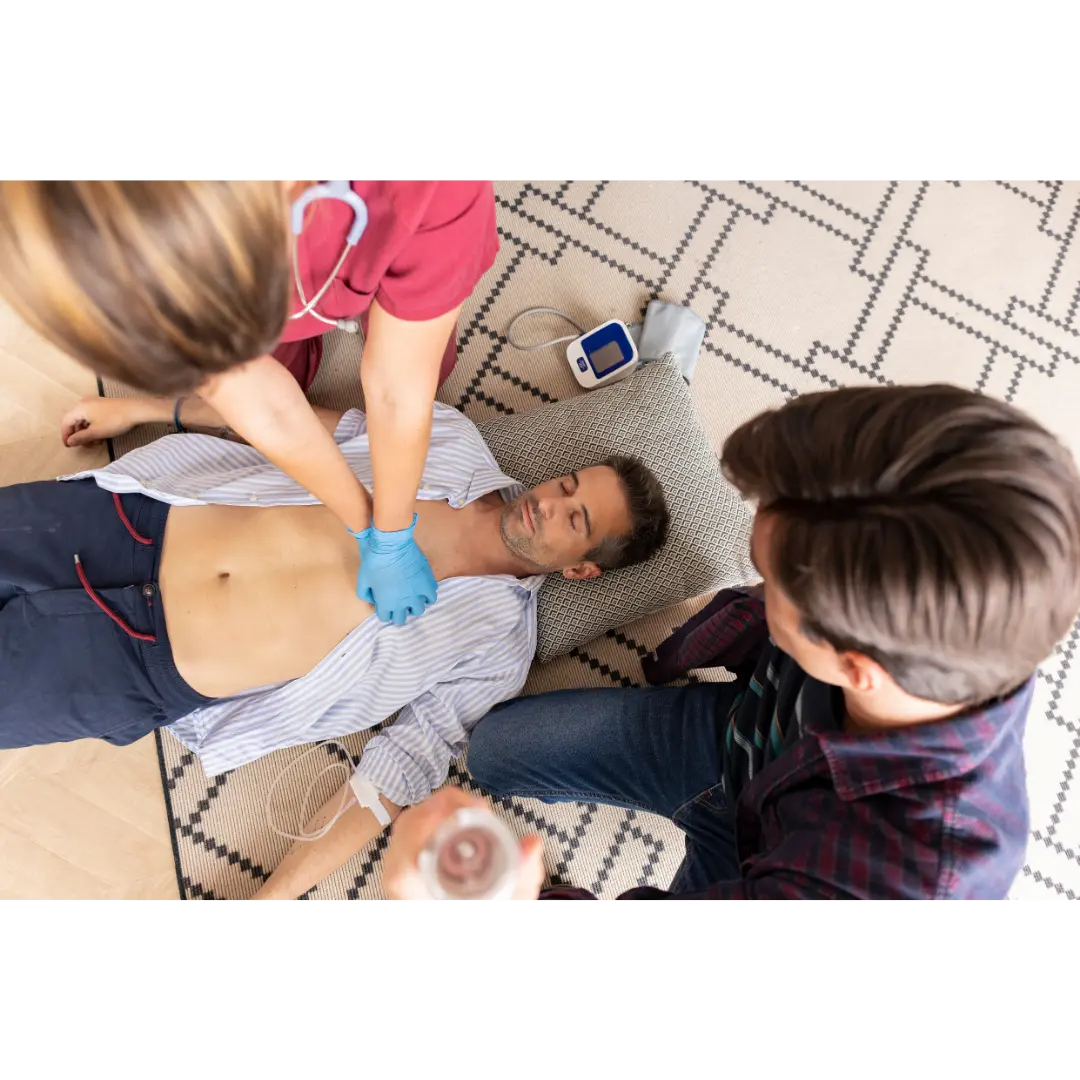
BLS for Infants: Focused Methods for Little Ones
Identifying Cardiac Arrest in Children
Recognizing cardiac arrest in children demands swift action, as their smaller bodies can deteriorate rapidly without intervention. When assessing a child for cardiac arrest, it’s crucial to be vigilant for subtle signs that may indicate a life-threatening situation. Look for sudden collapse, which may occur during physical activity or even while at rest. Unresponsiveness is another key indicator; if a child does not respond to verbal cues or gentle stimuli, it could signal a critical medical emergency. Additionally, observe for abnormal breathing patterns such as gasping, agonal respirations, or the absence of breathing altogether. Promptly recognizing these signs can expedite the initiation of life-saving measures.
Adjusted Chest Compressions
Chest compressions for children require a delicate balance of force and gentleness to effectively circulate blood and oxygen throughout their growing bodies. When performing chest compressions on a child, position yourself beside or slightly above the child’s chest. Utilize the heel of one hand for younger children or both hands for older children to deliver compressions. Apply pressure to the lower half of the sternum, aiming for a depth of approximately 2 inches, which is about one-third to one-half the depth of the child’s chest. It’s essential to maintain a steady rhythm and depth, allowing for full chest recoil between compressions to optimize blood flow.
Controlled Rescue Breaths
Delivering rescue breaths to children requires careful attention to ensure adequate ventilation without causing harm. Position the child on his or her back and tilt the head slightly backward to open the airway. With a proper seal, cover both the child’s mouth and nose with your mouth, creating an airtight seal. Administer gentle breaths, watching for the rise and fall of the child’s chest with each breath. Avoid excessive force to prevent overinflation of the lungs, which could lead to complications such as gastric distension. Remember to maintain the correct ratio of compressions to breaths, prioritizing high-quality chest compressions as the foundation of effective CPR for children.
By adapting BLS techniques to suit the unique needs of children, responders can optimize outcomes and increase the chances of survival in pediatric emergencies. Through ongoing education, practice, and dedication to excellence in care, we can ensure that every child receives the best possible chance of recovery in critical situations.
Conclusion: Empower Yourself with Essential BLS Skills
Mastering BLS CPR for different age groups is not just a skill; it’s a responsibility that can profoundly impact lives. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a first responder, or a concerned individual, being prepared to administer BLS effectively is crucial. By staying informed about the latest guidelines and best practices, you can enhance your ability to provide timely and efficient care in emergency situations.
Furthermore, regular practice and training are essential components of maintaining proficiency in BLS techniques. Participating in CPR and BLS certification courses, conducting mock scenarios, and staying up-to-date with refresher training sessions can help reinforce your skills and build confidence in your ability to respond effectively to cardiac emergencies.
Moreover, spreading awareness about the importance of BLS within your community can contribute to a safer and more resilient society. Encouraging others to learn BLS techniques, organizing training sessions, and advocating for widespread access to CPR training can empower more people to become potential lifesavers.
In essence, mastering BLS for different age groups is not just about acquiring knowledge; it’s about taking proactive steps to be prepared for emergencies and making a difference when it matters most. By prioritizing readiness, continuous learning, and community engagement, we can collectively work towards creating a world where everyone has the skills and confidence to save lives.
AHA BLS CPR & AED Classes
About Author:
admin
Recent Posts
- Top Industries in Denver, CO That Require CPR Certification
- Stay Certified: CPR for Personal Trainers & Coaches in Denver
- Infant CPR Training for Babysitters and Nannies in Denver, CO
- The Importance of CPR and AED Training in Denver, CO Workplaces
- Why Every Parent in Denver, CO Should Take an Infant & Child CPR Class