Why the American Heart Association Defines CPR Training

TLDR (Too Long; Didn’t Read)
The American Heart Association (AHA) is the gold standard authority for CPR and resuscitation science, backed by over a century of research.
- Mission: To fund research, fight heart disease/stroke, and set definitive, evidence-based guidelines for life-saving care globally.
- AHA vs. CPR/BLS: CPR is the basic skill; BLS (Basic Life Support) is the advanced professional certification that includes CPR and AED use; AHA Certification is the credential that validates the training is high-quality and science-backed.
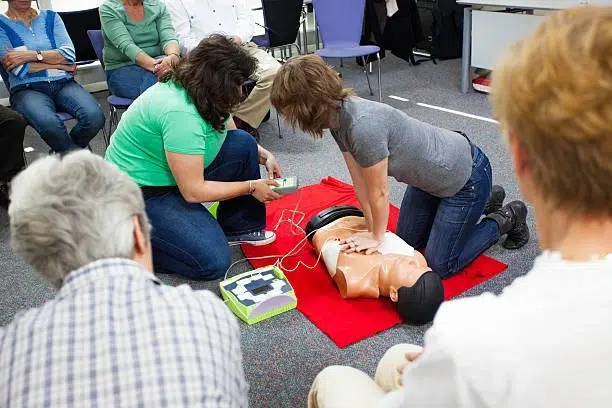
- Why It Matters: AHA certification is the most widely accepted credential by employers (especially in healthcare), ensuring you learn the current, effective techniques required to save a life. You must complete a mandatory hands-on session to get certified.
- Next Step: Get certified with an AHA-approved Training Site like CPR Classes Near Me Washington DC to gain the skills and credential employers trust.
Why is the American Heart Association the gold standard for CPR training?
In the United States, hundreds of thousands of cardiac arrests happen outside of a hospital setting every year. These critical moments often rely on immediate action by an everyday hero, a bystander. This is where the American Heart Association (AHA) steps in.
But what exactly is the American Heart Association? You may know them from the ubiquitous red-and-white shield logo or from the certification card you need for work. In reality, the AHA is far more than a certifying body; it is a global engine for scientific discovery and public health advocacy.
The AHA is the relentless force driving the improvement of cardiovascular health worldwide. Its mission touches everything from groundbreaking medical research to setting the definitive, evidence-based standards for life-saving skills like Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR).
For anyone seeking a reliable, high-quality CPR credential, particularly the Basic Life Support (BLS) certification, the AHA is the benchmark. Its commitment to science and education ensures that when you choose an AHA-certified course, like those offered by CPR Classes Near Me Washington DC, you’re learning the most effective techniques available to save a life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the history, mission, impact, and unparalleled authority of the American Heart Association, explaining why its guidelines are the gold standard for resuscitation science and why holding an AHA eCard is the most valuable credential you can earn.
Why was the American Heart Association founded and how did it begin?
The story of the American Heart Association stretches back over a century, beginning at a time when physicians were largely resigned to the limitations of treating heart disease.
The organization was formally founded in Chicago on June 10, 1924. It was started by six pioneering cardiologists and social workers who believed that scientific research, prevention, and public education could lead to better outcomes for patients.
- A Time of “Ignorance”: One of the founders, Dr. Paul Dudley White, famously described the early years as a period of “almost unbelievable ignorance” about cardiovascular disease. Heart disease was already America’s number one killer, yet treatment often amounted to mandatory bed rest.
- A Shift in Focus (1948): The organization was initially established as a professional scientific society for doctors. However, a major reorganization in 1948 transformed the AHA into a nationwide voluntary health organization. This shift opened the doors for thousands of volunteers and supporters, allowing the organization to focus on crucial public fundraising and widespread community outreach.
- Early Milestones: This reorganization paved the way for the AHA to award its first research grant and launch its first public campaign, “Heart Week,” cementing its role as a leader in both science and public engagement.
Since then, the AHA has funded groundbreaking research that led to major medical advances, including linking dietary fat and cholesterol to heart disease (1956) and contributing to the development of the artificial heart valve and the fully implanted pacemaker (1957).
What is the American Heart Association’s core mission and how does it impact public health?
The modern American Heart Association operates under a powerful, clearly defined mission, updated in 2018: “To be a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives.”
This mission is supported by strategic work across five key pillars, which collectively have a profound impact on public health globally:
- Research Funding: The AHA is the nation’s largest non-government funder of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular research. Since 1949, it has invested over $6.1 billion in science, driving discoveries that impact everything from medication development to surgical techniques and resuscitation protocols.
- Heart and Brain Health: The organization promotes consumer education on healthy living, nutrition, exercise, and preventative care. Programs like Go Red for Women (launched in 2004) specifically raise awareness that heart disease is the leading cause of death for women.
- Equitable Health: The AHA actively works to address health disparities rooted in societal structures, aiming to ensure equitable delivery and accessibility of life-saving care and resources, especially in low-resource settings.
- Advocacy: The AHA champions stronger public health policies, including fighting for smoke-free environments, improving emergency medical services (EMS) systems, and promoting quality standards in hospitals.
- Professional Education and Development: This pillar is critical for the general public and professionals alike. The AHA trains millions of people annually in CPR and advanced life support, ensuring that healthcare providers and lay rescuers have consistent, evidence-based training.
How does the AHA set the gold standard for resuscitation science?
The American Heart Association holds its ultimate authority through its role as the global leader in Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) guidelines. These guidelines are not arbitrary; they are the foundation for virtually every resuscitation course taught around the world.
The Foundation of Evidence
Every five years, the AHA publishes comprehensive Guidelines for CPR and ECC, such as the 2025 Guidelines, following an exhaustive review of global resuscitation science. This process ensures that the techniques taught are the most current and effective available.
Key elements of the AHA’s scientific authority include:
- Evidence-Based Practice: The guidelines are developed based on an unbiased, rigorous review of scientific literature, frequently in collaboration with other international organizations like the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR).
- The Chain of Survival: The AHA defines the necessary sequence of actions required to maximize the survival rate of someone experiencing cardiac arrest. This sequence outlines the precise, time-sensitive steps that must be taken, including:
- Immediate recognition of cardiac arrest and activation of the emergency response system.
- Early CPR with emphasis on high-quality chest compressions.
- Rapid defibrillation (using an AED).
- Effective advanced life support and post-cardiac arrest care.
- Recovery.
- The Get With The Guidelines (GWTG) Program: This hospital-based quality improvement program helps hospitals implement the latest AHA guidelines and track data, directly turning research into practice and constantly refining resuscitation efforts in clinical settings.
The resulting guidelines ensure that a person certified in Washington DC, or anywhere in the U.S., is trained using the exact same standard of care established by the world’s top cardiologists and resuscitation scientists.
What is the difference between CPR, BLS, and AHA certification?
When looking for training, you will often encounter three key terms: CPR, BLS, and AHA. While they are related, they represent different levels of skill and credentialing.
1. CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
CPR is the fundamental skill set. It is an emergency procedure performed when the heart stops beating, aiming to keep blood (and thus oxygen) flowing to the brain and other vital organs until professional medical help arrives.
Key components of CPR taught in all AHA courses include:
- Hands-on Chest Compressions: Focusing on high-quality, continuous compressions at the correct depth and rate.
- Rescue Breaths (Ventilations): Providing air to oxygenate the victim’s blood.
- Choking Relief: Techniques for clearing airway obstructions in various age groups.
2. BLS (Basic Life Support)
BLS is the higher-level, professional credential that incorporates CPR, but with additional focus and complexity necessary for those working in a healthcare or regulated setting. The AHA BLS Provider Course is the industry standard.
BLS goes beyond basic CPR by teaching:
- Advanced Assessment: Identifying signs of cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, and stroke.
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Proficiency: Detailed training on the safe and effective use of an AED.
- Team Dynamics: Effective communication and collaboration within a resuscitation team setting, crucial for healthcare teams.
- Multi-Age Proficiency: Training that is robust and detailed for adults, children, and infants.
3. AHA Certification
AHA Certification is the credential that validates a person has mastered the skills and cognitive material for BLS (or other AHA courses) according to the latest, scientific guidelines.
AHA certification is the most trusted because:
- It means the instructor and curriculum were audited and approved by the highest authority in resuscitation science.
- It ensures the training includes a mandatory, in-person, hands-on skills session, which most employers require.
- It is recognized nationally, making it a portable and reliable credential for any professional.
Why is AHA certification the most trusted credential for employers nationwide?
In the professional world, the type of CPR certification you hold matters immensely. Many employers specify that they will only accept a certification from the American Heart Association, a demand rooted in quality assurance and legal compliance.
1. Guaranteed Acceptance and Standardization
The most compelling reason to choose AHA certification is its universal acceptance.
- Healthcare Industry: For Nurses, EMTs, CNAs, and Medical Office Personnel, the AHA BLS Provider card is the de facto requirement. Hospitals and clinics rely on the AHA’s strict, scientifically validated training curriculum.
- Regulated Industries: Professions subject to health and safety regulations, such as Childcare Providers, Teachers, and Physical Therapists, rely on the AHA’s credential due to its alignment with federal standards. The certification is often OSHA approved, meeting the requirements for various safety-sensitive jobs, including construction workers and flight attendants.
By choosing the AHA, you eliminate the risk of an employer rejecting your eCard because they don’t recognize the training provider or curriculum.
2. Commitment to Hands-On Skills
Unlike some online-only courses that are often rejected by employers, AHA training models emphasize proficiency. The AHA strongly advocates for Blended Learning (HeartCode®) which combines:
- Online Cognitive Module: The student learns the necessary science, theory, and algorithms at their own pace.
- In-Person Skills Session: A mandatory, hands-on session with a certified instructor and training manikins is required to prove competence in chest compressions and rescue breathing.
Training sites like CPR Classes Near Me facilitate this process, ensuring that every student leaves with the tactile skills necessary to act decisively in an emergency.
3. Quick and Convenient Certification
For busy professionals in the nation’s capital, speed is essential. One key benefit of choosing an accredited training site in the Washington DC area is the immediate issuance of the certification.
- Same-Day eCards: Upon successful completion of the course, participants often receive their official AHA BLS eCard the same day. This immediate credentialing is vital for those who need to start a new job or maintain current compliance without delay.
Beyond BLS, what other life-saving programs does the AHA offer?
While Basic Life Support (BLS) is the most widely known certification, the AHA offers a full spectrum of Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) courses tailored to various professional levels.
These programs all operate under the same high-quality, evidence-based umbrella established by the AHA:
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS): Designed for healthcare professionals who either direct or participate in the management of cardiopulmonary arrest or other cardiovascular emergencies. ACLS involves advanced airway management, pharmacology, and interpreting ECGs (electrocardiograms).
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS): Similar to ACLS but focused entirely on managing life-threatening emergencies in infants and children, including resuscitation, rhythm disturbances, and shock.
- Heartsaver® Courses: These are courses specifically designed for the general public, non-healthcare workers, or those who need to meet OSHA requirements (e.g., teachers, daycare workers, corporate staff). They include:
- Heartsaver CPR AED
- Heartsaver First Aid
- Heartsaver Pediatric First Aid CPR AED
The comprehensive nature of the AHA’s offerings ensures that everyone can find the certification level they need, all backed by the same scientific authority.
What are the American Heart Association’s goals for improving survival rates?
The work of the AHA is far from complete. Despite its historical success, survival rates for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) remain critically low, around 9.1% for adults. The AHA recognizes this public health crisis and has set ambitious goals to combat it.
The AHA’s Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) 2030 Impact Goals focus on measurable improvement in several key areas:
- Increasing Bystander CPR Rates: Currently, only about 40% of OHCA victims receive immediate bystander CPR. The AHA aims to increase this rate significantly by expanding training accessibility and awareness, especially in public settings.
- Improving Access and Equity: Data shows significant disparities in cardiac arrest survival based on geography (rural vs. metropolitan) and race/ethnicity. The AHA is prioritizing equitable delivery of life-saving interventions across the Chain of Survival to eliminate these disparities.
- Early Defibrillation: The goal is to substantially increase the proportion of individuals who have an AED applied before the arrival of emergency services. Immediate CPR and AED use can double or even triple a victim’s chance of survival.
- Establishing Cardiac Arrest as a Reportable Disease: This goal seeks to mandate standardized reporting of outcomes from various sources, enabling the AHA and other organizations to better track progress, identify gaps in care, and refine future guidelines.
These goals emphasize that every person trained in CPR, whether a Washington DC resident or a medical professional, contributes directly to a massive, national public health effort spearheaded by the AHA.
Conclusion
The American Heart Association is the single most important organization in the fight against cardiovascular disease and stroke. From its modest beginnings in 1924 to its current role as a global scientific powerhouse, the AHA has defined the modern approach to prevention, treatment, and emergency response.
For professionals, the choice is clear: an AHA certification is not just a piece of paper; it represents adherence to the highest standard of care, ensuring you have the proven, science-backed skills that employers trust and that victims need. It is a commitment to being part of the solution to the nation’s leading cause of death.
By getting certified with an AHA-approved Training Site, you are empowering yourself and your community with a skill set backed by a century of research and dedication.
Ready to join the relentless force for longer, healthier lives?
Schedule Your CPR Certification with CPR Classes Near Me Today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Section
What is the most common CPR certification offered by the American Heart Association?
The most common and widely recognized certification offered by the American Heart Association is the Basic Life Support (BLS) Provider Certification. This course is specifically designed for healthcare professionals and students who need a comprehensive certification covering CPR and AED use for adults, children, and infants. However, for non-healthcare professionals (teachers, corporate staff, general public), the AHA also offers its popular Heartsaver courses, which focus on fundamental CPR, AED, and First Aid skills.
How long does an American Heart Association CPR certification remain valid?
An American Heart Association CPR or BLS certification is typically valid for two years. The two-year validity period ensures that certified professionals and lay rescuers refresh their knowledge and skills regularly and stay current with the AHA’s latest resuscitation science and guidelines, which are frequently updated. After this period, a renewal course is required.
Is the BLS certification the same as standard CPR certification?
No, BLS (Basic Life Support) is more comprehensive than a standard CPR certification. Standard CPR (often taught in Heartsaver courses) focuses mainly on chest compressions and rescue breaths for a single rescuer. BLS is an advanced certification that encompasses all CPR skills but adds: 1) advanced assessment and rescue techniques; 2) proficient use of an AED; 3) recognition of advanced life-threatening emergencies; and 4) essential skills for working effectively within a resuscitation team. BLS is generally mandatory for clinical healthcare roles.
Can I take an American Heart Association CPR certification course entirely online?
No, you cannot receive a full, accredited AHA CPR or BLS certification entirely online. The AHA requires a mandatory hands-on skills session to ensure competency in performing the physical techniques of chest compressions and rescue breathing. While you can complete the cognitive (lecture) portion of the course through the AHA’s online platform (known as Blended Learning or HeartCode®), you must still attend an in-person session with an AHA Instructor to successfully demonstrate your skills before receiving your eCard.
Why do employers often require the American Heart Association certification over other providers?
Employers overwhelmingly prefer the AHA certification because it is universally recognized as the gold standard, backed by over 100 years of research. The AHA is the primary organization that writes and updates the scientific guidelines for CPR and Emergency Cardiovascular Care used throughout the United States. Requiring AHA certification ensures that employees are trained in the most current, evidence-based techniques, which mitigates liability and guarantees a standardized level of emergency preparedness.