CPR Certification Requirements by Industry in San Diego, CA

CPR Certification Requirements by Industry in San Diego, CA

Whether you work in healthcare, education, construction, or childcare, knowing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) can save lives. But did you know that CPR certification requirements can vary significantly depending on the industry you’re in, especially in a dynamic city like San Diego, CA? This blog will walk you through the industry-specific CPR certification requirements you need to be aware of in San Diego. Whether you’re an employer or an employee, understanding these standards will keep you compliant, confident, and ready to respond in emergencies.
Why CPR Certification Matters Across Industries
CPR certification is not just a checkbox for compliance; it’s a critical skill that can make the difference between life and death. Different industries face different risks and regulatory demands, so the requirements for CPR certification vary accordingly.
San Diego, with its mix of industries and stringent safety regulations, requires professionals in certain sectors to obtain CPR certification that fits their specific job functions and workplace environments. Ensuring your CPR training meets these demands can protect your workforce and your business from liability.
Healthcare Industry
Healthcare workers in San Diego face the most rigorous CPR certification requirements. Hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and emergency medical services typically require:
- Basic Life Support (BLS) Certification: This includes CPR and Automated External Defibrillator (AED) training designed specifically for healthcare professionals.
- Pediatric CPR: For those working with infants and children.
- Recertification: Typically every two years to ensure skills stay sharp.
Compliance with standards set by bodies like the American Heart Association (AHA) is mandatory. Healthcare employers in San Diego usually require employees to carry current BLS certification to maintain licensing and credentialing.
Education Sector
Teachers, school staff, and daycare workers in San Diego must also be prepared to handle emergencies. CPR requirements here include:
- Adult and Pediatric CPR Certification: Since schools serve children primarily, pediatric CPR is often a must.
- AED Training: Many schools are equipped with AEDs, so knowing how to operate one is essential.
- State-Specific Mandates: California law mandates CPR training for school employees in many districts, with recertification typically every two years.
Schools and childcare centers in San Diego often provide CPR classes onsite or partner with local providers to ensure staff compliance.
Hospitality Industry
San Diego’s vibrant hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and event venues, also has tailored CPR requirements:
- Basic CPR and AED Training: Many employers require certification for staff members who are most likely to encounter medical emergencies, such as managers and front-line staff.
- OSHA Compliance: Restaurants and hospitality venues must follow Occupational Safety and Health Administration guidelines, which include having trained personnel on site.
- Renewal Cycles: Certification usually requires renewal every two years to maintain readiness.
Hotels and event venues often encourage widespread CPR certification to create a safer environment for guests and employees alike.
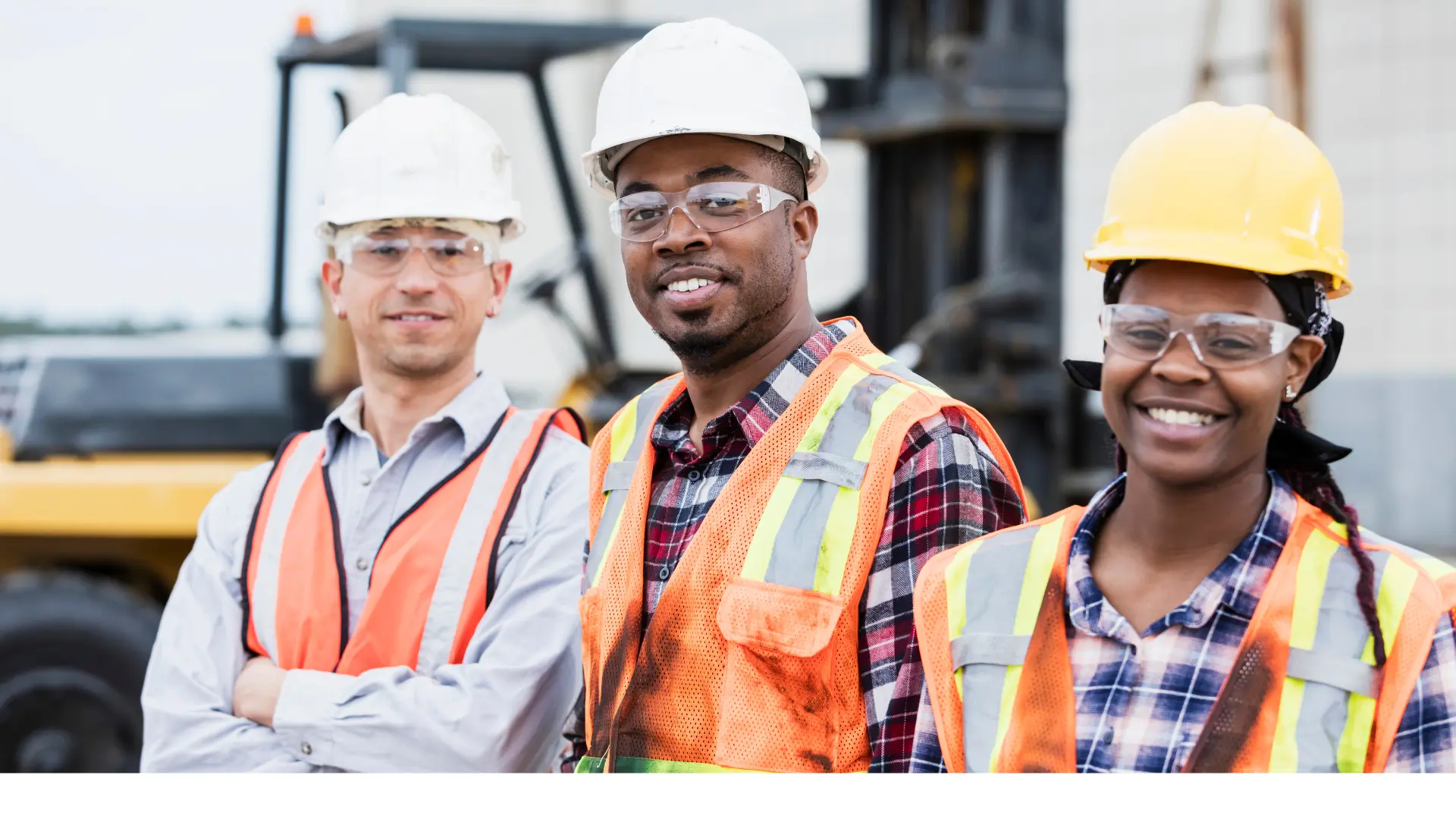
Construction and Industrial Work
Construction sites and industrial workplaces in San Diego involve higher physical risks, so CPR certification here is crucial:
- CPR and AED Training: OSHA requires construction employers to provide first aid training, including CPR certification, to at least some workers.
- Emergency Response Training: Many companies integrate CPR certification with other safety protocols like fall prevention and hazard communication.
- Regular Recertification: Typically required every two years.
Because San Diego is home to many construction projects and industrial operations, onsite CPR training classes are often available to keep workers compliant and safe.
Childcare and Fitness Industries
Childcare centers and fitness facilities also require CPR certification tailored to their environments:
- Pediatric and Adult CPR: Childcare workers must have pediatric CPR due to the age group they serve, while fitness trainers often need adult CPR.
- AED Use: Many gyms and childcare centers have AEDs onsite.
- Recertification Requirements: Generally every two years.
San Diego providers often offer flexible class schedules for childcare and fitness workers, helping them meet certification requirements without disrupting their busy routines.
How to Choose the Right CPR Certification Class in San Diego
Selecting the right CPR course is key to meeting industry-specific requirements:
- Accreditation: Ensure the course is recognized by the American Heart Association or equivalent bodies.
- Industry Focus: Choose courses tailored to your industry (e.g., BLS for healthcare, pediatric CPR for childcare).
- Location and Timing: Look for CPR classes near you in San Diego with flexible scheduling.
- Certification Validity: Confirm that the certification meets your employer or licensing body’s standards.
Conclusion
No matter what industry you’re in, CPR certification is an essential part of workplace safety in San Diego, CA. Understanding your industry’s specific requirements ensures you stay compliant, protect your coworkers, and contribute to a safer community.
Ready to get certified or renew your CPR training? Contact CPR Classes Near Me today for accessible, expert-led CPR certification courses tailored to your industry’s needs in San Diego. Stay prepared, because every second counts in an emergency.
AHA BLS CPR & AED Classes
FAQ
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!