Mastering First Aid Training: A Vital Skill for Life

Mastering First Aid Training: A Vital Skill for Life

In the hustle and bustle of daily life, accidents and emergencies can strike unexpectedly. From minor cuts and scrapes to choking hazards and life-threatening situations, being prepared to respond effectively can make a world of difference. This is where First Aid Training comes in – a powerful tool that equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to act confidently in critical moments.
Why First Aid Training Matters
First Aid Training is more than just learning a few basic techniques. It’s about empowering yourself to take charge in an emergency, potentially saving lives and preventing further harm. Here’s a closer look at the significant impact First Aid Training can have:
- Saves Lives and Prevents Further Harm: Early intervention during emergencies is crucial. First Aid Training equips you to assess the situation, administer basic life support measures like CPR, and provide initial care for injuries until medical professionals arrive. This prompt action can prevent minor injuries from worsening and even save lives in critical situations.
- Empowers Individuals to Act Confidently: Imagine witnessing a choking incident or someone experiencing a sudden collapse. First Aid Training instills the knowledge and practical skills to handle a wide range of medical situations. This newfound confidence allows you to take control of the emergency, providing essential comfort and support to the injured or ill person.
- Reduces Recovery Time and Complications: The right first aid intervention can significantly impact a person’s recovery. For instance, proper wound cleaning and dressing techniques can minimize the risk of infection, while proper fracture immobilization can prevent further displacement of the bone. By knowing how to react effectively, you can play a vital role in promoting faster healing and reducing potential complications.
- Creates a Safer Environment: A community empowered with First Aid Training fosters a safer environment for everyone. Whether at home, work, school, or in public spaces, individuals with first aid skills can contribute significantly to emergency preparedness and response. This collective knowledge creates a safety net, ensuring a quicker and more effective response during unforeseen situations.
Who Should Consider First Aid Training?
First Aid Training is a valuable skill for everyone, regardless of age, profession, or background. Here’s why it’s particularly beneficial for certain individuals:
- Parents and Caregivers: Children are naturally curious and adventurous, and accidents are a common occurrence. Being First Aid certified allows parents and caregivers to respond calmly and effectively to childhood injuries, from minor scrapes to choking hazards.
- Teachers and Coaches: Schools and sports facilities are environments with a heightened risk of minor injuries. First Aid trained teachers and coaches can ensure the safety and well-being of students and athletes by providing immediate care for cuts, bruises, sprains, and other common injuries.
- Workplace Safety Personnel: Accidents can happen anywhere, even in controlled environments like workplaces. Equipping employees with First Aid Training creates a safer work environment and empowers them to respond effectively to potential emergencies.
- The General Public: First Aid knowledge is a valuable asset for anyone. By taking a First Aid Training course, you gain the ability to help those in need during unexpected emergencies, be it a stranger on the street, a neighbor experiencing a medical episode, or a loved one facing a sudden injury.
What Does First Aid Training Entail?
First Aid Training courses typically cover a comprehensive range of topics designed to equip you with the essential skills to manage various medical emergencies. Here’s a breakdown of some of the key areas covered in most First Aid Training programs:
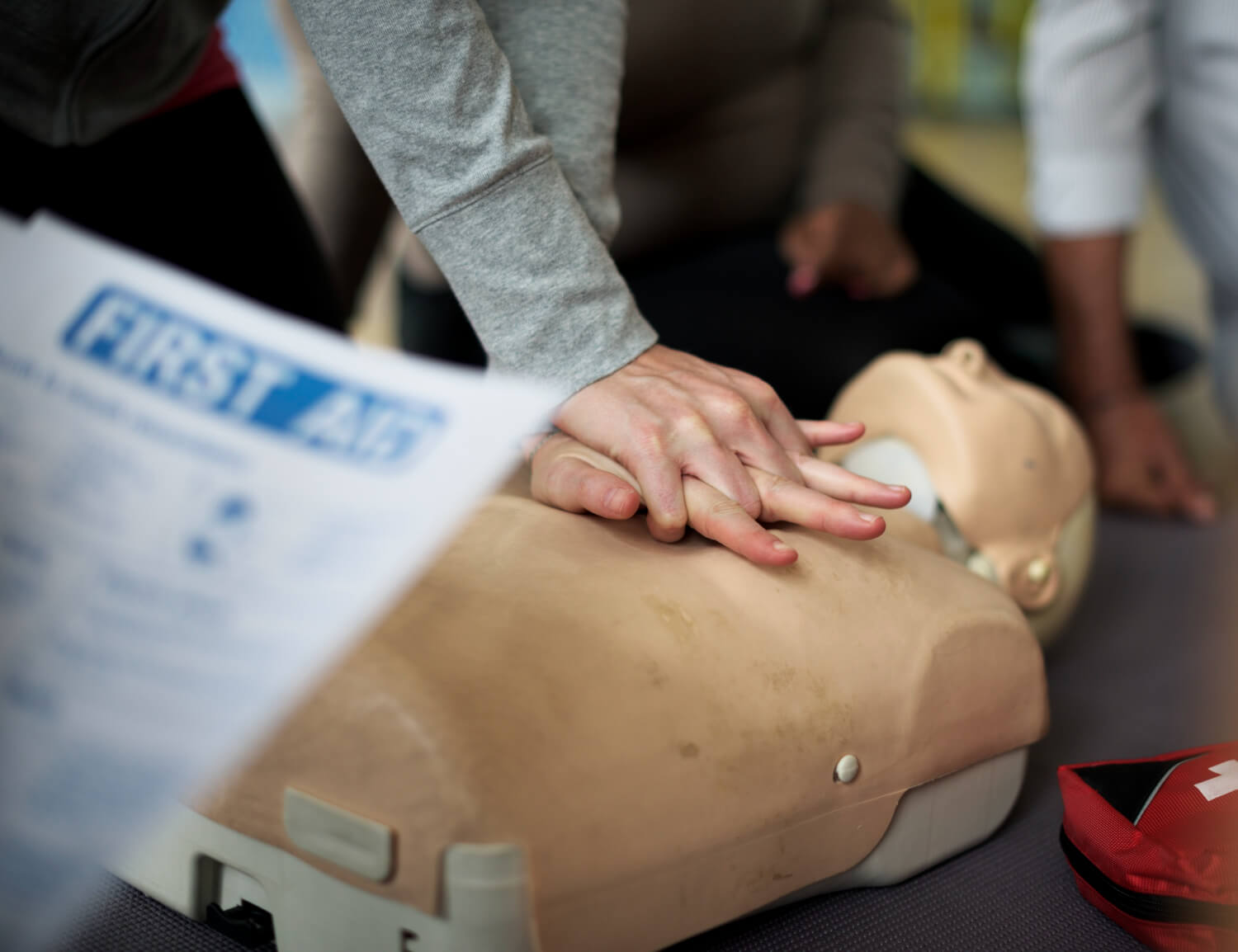
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): This life-saving technique involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain circulation and oxygen flow in a person experiencing cardiac arrest. First Aid Training equips you with the skills to perform CPR effectively for adults, children, and infants.
- Basic Wound Care: Learning how to properly clean, dress, and bandage wounds is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. First Aid Training covers various wound types, cleaning techniques, and proper bandaging methods.
- Choking Relief Maneuvers: Choking emergencies can be life-threatening, particularly for young children. First Aid Training equips you with the Heimlich maneuver and other techniques to dislodge obstructions from the airway in adults, infants, and pregnant women.
- Management of Bleeding: Learning how to control bleeding effectively is essential in various injury scenarios. First Aid Training covers methods for applying direct pressure, using pressure points, and utilizing improvised dressings to control bleeding.
- Management of Musculoskeletal Injuries: Accidents can often lead to sprains, strains, and fractures. First Aid Training teaches you how to identify these injuries, provide support and immobilization, and prevent further complications.
- Management of Burns: Burns can be extremely painful and pose a risk of infection. First Aid Training covers different types of burns, proper cooling techniques, and methods to minimize further damage.
- Management of Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, can be life-threatening. First Aid Training teaches you to recognize the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as difficulty breathing, swelling, and hives. You’ll also learn how to administer an epinephrine auto-injector, a medication that can reverse a severe allergic reaction.
- Management of Stroke: Strokes occur when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted. Recognizing the signs of a stroke (facial drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulty) and calling emergency services immediately is crucial. First Aid Training can help you identify these warning signs and act swiftly.
- Management of Diabetic Emergencies: Both diabetic emergencies – hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) – require prompt action. First Aid Training equips you to recognize the signs and symptoms of each condition, administer glucagon (in case of hypoglycemia) if necessary, and provide basic support until medical help arrives.
- Management of Seizures: Seizures can be a frightening experience for both the person experiencing them and those witnessing them. First Aid Training teaches you how to stay calm, ensure the person’s safety by removing nearby hazards, and time the duration of the seizure.
- Management of Fainting: Fainting is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a sudden drop in blood flow to the brain. First Aid Training equips you to assess the situation, position the person safely, and ensure proper airway management until they regain consciousness.
- Management of Environmental Emergencies: First Aid Training also covers how to respond to environmental emergencies like heatstroke, hypothermia, and exposure to toxic substances. You’ll learn about recognizing the signs and symptoms of these conditions and providing initial care until medical assistance arrives.
Additional Considerations When Choosing a First Aid Training Course
Besides the core curriculum, several factors come into play when choosing a First Aid Training course. Here are some key considerations:
- Course Format: First Aid Training courses are offered in various formats, including in-person classes, online modules, and blended learning programs that combine online learning with hands-on practice sessions. Consider your learning style and schedule when choosing a format. In-person classes offer the benefit of direct instructor guidance and practical skill development, while online courses provide flexibility and can be completed at your own pace. Blended learning programs offer a combination of both approaches.
- Course Duration and Certification: First Aid Training courses can range from a few hours to several days, depending on the level of detail and the certifications offered. Basic First Aid courses typically cover essential life-saving skills like CPR and choking relief maneuvers. More comprehensive courses may delve deeper into specific topics like wound care, managing burns, and first aid for sudden medical conditions. Ensure the course you choose aligns with your learning objectives and desired level of certification.
- Trainer Credentials: It’s crucial to choose a First Aid Training program offered by a reputable organization with certified instructors. Look for trainers affiliated with recognized organizations like the American Red Cross, American Heart Association, or other accredited institutions. These organizations ensure trainers possess the necessary expertise and adhere to the latest First Aid guidelines.
- Course Renewal Requirements: Most First Aid certifications expire after a specific period, usually one to two years. Choose a program that provides clear information on renewal requirements and offers refresher courses to maintain your certification.
The Benefits of Ongoing Practice and Refresher Training
First Aid skills, like any other skill, can deteriorate over time without regular practice. Here’s why ongoing practice and refresher training are essential:
- Maintaining Muscle Memory: First Aid techniques often involve a series of steps performed in a specific sequence. Regular practice helps to solidify these steps in your muscle memory, ensuring you can react quickly and effectively during an emergency.
- Building Confidence: Confidence is key in an emergency situation. By practicing First Aid skills regularly, you remain comfortable and confident in your ability to take decisive action.
- Staying Up-to-Date: Medical guidelines and best practices for First Aid can evolve over time. Refresher training ensures you stay updated on the latest recommendations and techniques.
- Reinforcing Knowledge Retention: Regular practice helps to solidify your knowledge and understanding of First Aid principles. Refresher training provides an opportunity to revisit key concepts and address any areas where you may have developed knowledge gaps.
Conclusion
First Aid Training is an invaluable investment in the well-being of yourself and those around you. By equipping yourself with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively in emergencies, you can potentially save lives, prevent complications, and contribute to a safer environment for everyone. Take the initiative to enroll in a First Aid Training course today and empower yourself to make a lasting difference.
Additional Tips:
- Look for First Aid Training programs offered in your community centers, workplaces, or health organizations.
- Consider taking a course specifically designed for your industry or area of interest, such as First Aid for childcare providers or wilderness first aid.
- Encourage your family members and loved ones to get First Aid certified as well.
- Invest in a well-stocked First Aid kit for your home, car, and workplace.
So, why wait? Take the first step and embark on your journey to becoming a proficient first aid responder today. Contact CPR Classes Near Me for the best First Aid Classes in your area.
About Author:
admin
Recent Posts
- The Shocking Statistics of Cardiac Arrest: A Cause for Awareness
- Unveiling the Emotional Rewards of Saving a Life: Understanding the Hero Effect
- CPR for Different Emergencies: Beyond Cardiac Arrest
- The Vitality of CPR Training and Certifications: Lifesaving Beyond Expectations
- Why You Should Take a CPR Class: The Power to Save a Life in Your Hands