Infant Safety: Pediatric CPR & First Aid for Raleigh Parents

The arrival of a new baby is an experience filled with profound joy, love, and, inevitably, a certain level of anxiety. As a new parent, your instinct is to protect your child at all costs. You baby-proof the house, install the perfect car seat, and research the safest sleep guidelines. Yet, many essential steps toward preparedness are often overlooked until it is too late. The most crucial investment you can make is not in gear or gadgets, but in your own knowledge and confidence to act when seconds count.
This preparation centers on obtaining specialized, hands-on training in pediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and comprehensive First Aid. For families in the Triangle area, gaining this certification locally in Raleigh is a foundational step in ensuring the utmost safety for your infant or toddler. By acquiring these skills, you are doing more than just earning a certificate; you are equipping yourself to be your child’s critical first line of defense during a medical emergency. The goal is simple: to transform moments of panic into opportunities for life-saving action.
Why is Infant-Specific CPR Training Essential for Raleigh Parents?
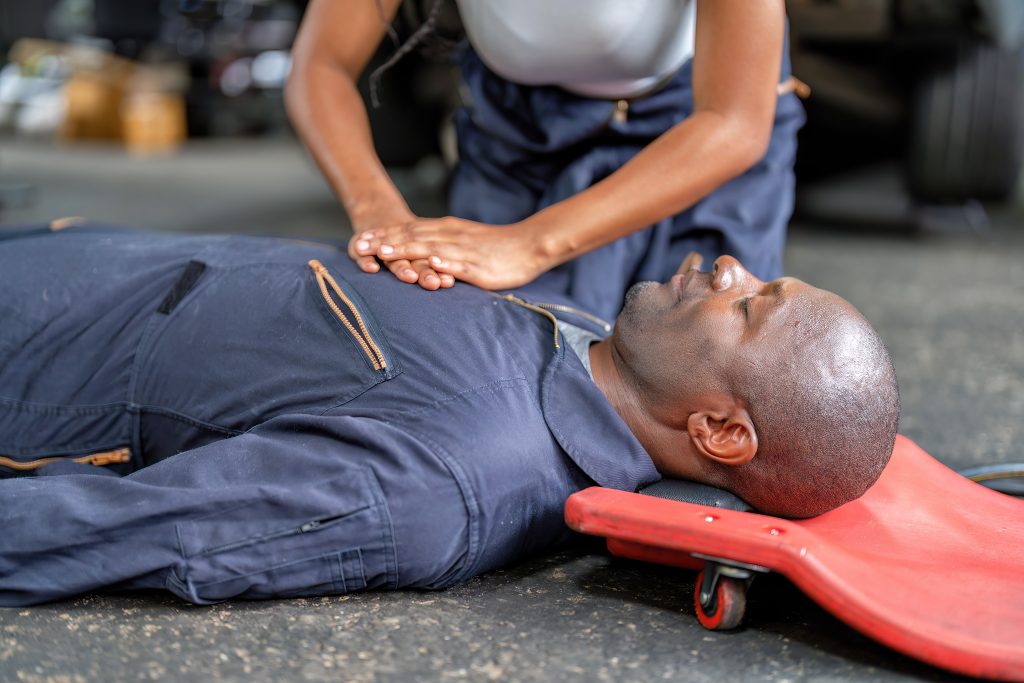
Standard adult CPR techniques are fundamentally different from those required for an infant, making specialized pediatric training an absolute necessity for new parents. An infant’s anatomy is delicate and unique, meaning mistakes in compression depth or force can lead to further injury. This is why generalized CPR training is not enough. You must learn the exact modifications needed to resuscitate a tiny body safely and effectively.
- Compression Depth: For an adult, chest compressions are deep and use the full weight of the rescuer. For an infant, the compression depth is far shallower—roughly one-third the depth of the chest, or about 1.5 inches.
- Hand Placement: While adults require the heel of one or two hands, infant CPR typically uses just two fingers placed directly on the breastbone, slightly below the nipple line.
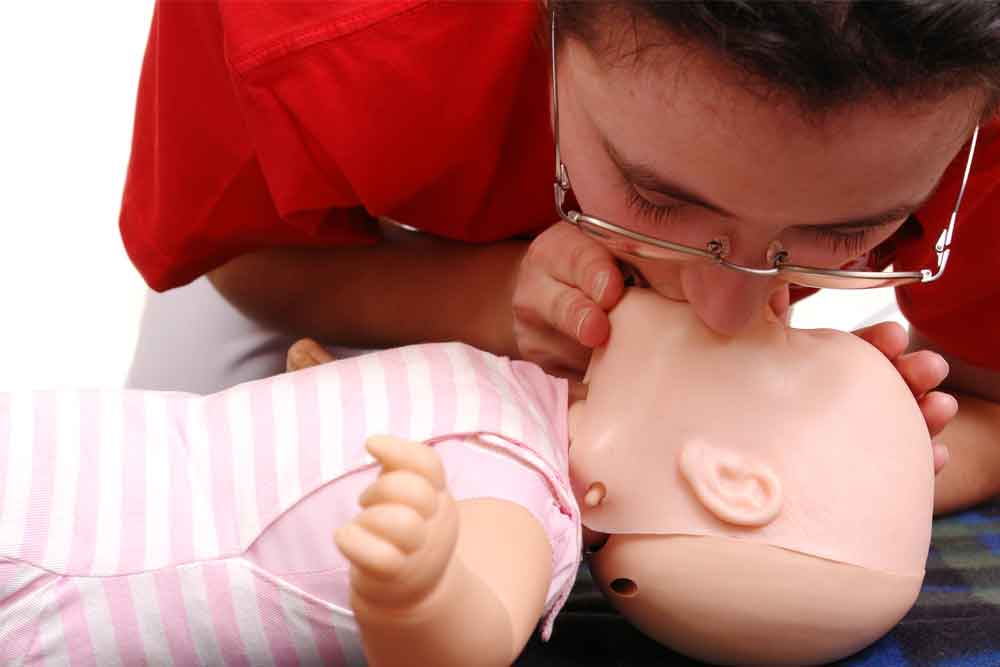
- Airway Management: An infant’s airway is extremely fragile. Over-tilting the head can actually obstruct the airway, meaning rescue breaths require a much gentler “puff” and a slight, controlled head tilt to maintain openness.
The American Heart Association (AHA) mandates specific techniques for infant resuscitation because quick, correct action significantly increases the chance of survival. With infants, cardiac arrest is most often the result of a respiratory problem, such as choking or suffocation, rather than a primary heart issue. This means intervening quickly to restore breathing is paramount. Training ensures you can execute these life-saving variations under stress, giving your child the best chance for a positive outcome until professional help arrives.
What Pediatric First Aid Essentials Go Beyond Basic CPR?
While CPR training addresses cardiac and respiratory arrest, pediatric first aid provides a broad spectrum of skills necessary for handling the vast majority of everyday childhood emergencies that are not immediately life-threatening. The most comprehensive classes for parents in Raleigh combine both certifications. This comprehensive preparedness is what truly gives parents peace of mind, allowing them to manage everything from a minor burn to a severe allergic reaction.
Pediatric First Aid covers essential skills, including the ability to identify and treat various common childhood ailments and injuries. These are the incidents that are far more likely to occur than full cardiac arrest.
Key First Aid Scenarios Covered for Parents:
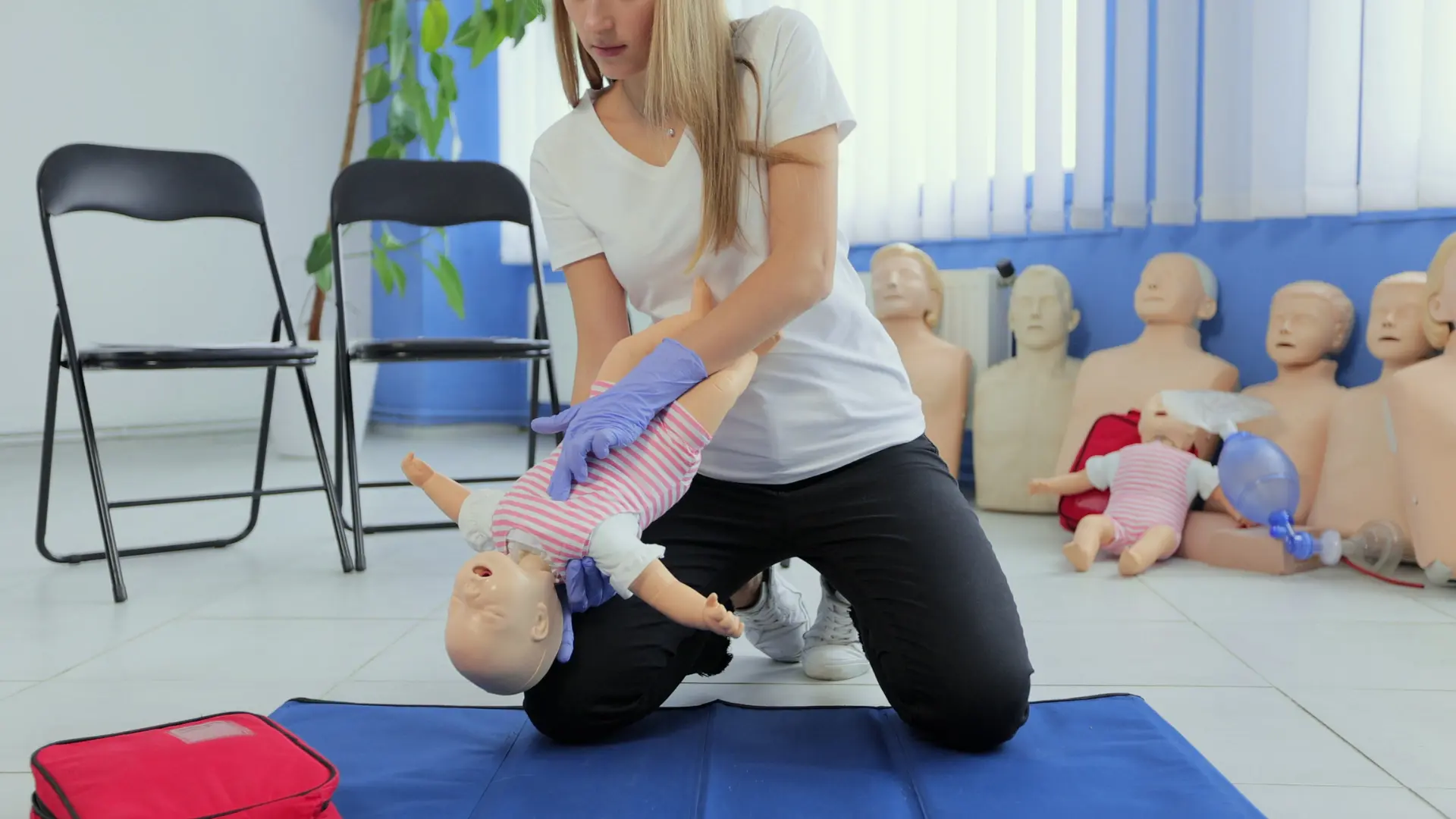
- Choking Relief: This is arguably the most common and terrifying scenario. You learn the specific sequence of five back blows and five chest thrusts for conscious infants, a crucial technique different from the adult Heimlich maneuver.
- Wound Care and Bleeding Control: Learn how to manage severe bleeding, properly dress minor cuts and scrapes, and determine when a wound requires professional suturing.
- Burns and Scalds: Understand the classification of burns and the immediate steps to take, such as cooling the area with running water and knowing when to call 911 for severe injuries.
- Poisoning Management: Learn how to recognize signs of accidental poisoning, what information to gather, and the correct procedure for contacting the Poison Control Center immediately.
- Fever and Febrile Seizures: Gain knowledge on how to monitor and manage high fevers in infants, and, most importantly, how to respond calmly and correctly if a febrile seizure occurs.
- Anaphylaxis and Severe Allergic Reactions: Learn the critical steps for recognizing a severe allergic reaction and practicing how to administer an epinephrine auto-injector device (like an EpiPen) if a child has a known allergy.
- Musculoskeletal Injuries: Training includes the R.I.C.E. method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) for treating sprains and strains, and how to immobilize a suspected fracture until medical help is available.
By mastering these diverse skills, parents transition from feeling helpless observers to confident first responders, ready to address a wide array of crises within the critical first minutes.
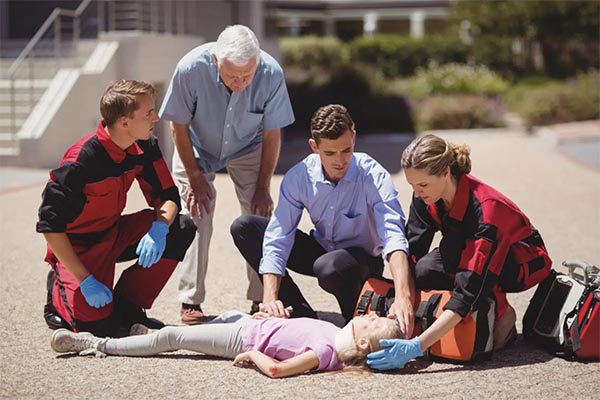
What Are the Most Common Life-Threatening Pediatric Scenarios New Parents Face?
New parents are right to worry about the “what-ifs,” and professional training focuses on the statistically most dangerous scenarios for children, often caused by accidental injury rather than illness. Understanding the most likely threats helps parents prioritize their vigilance and use their training effectively.
The Top Three Risk Categories for Infants and Young Children:
- Airway Obstruction (Choking and Suffocation):
- Choking is a primary concern, especially as babies start solids or begin exploring the world by placing small objects in their mouths (often around six months).
- Parents have a window of approximately 30 to 60 seconds to dislodge an obstruction before a child loses consciousness.
- Suffocation is a major factor in Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID). Safe sleep practices are preventive, but knowing infant CPR is the safety net should respiratory arrest occur.
- Drowning:
- For children aged one to four, drowning is tragically the leading cause of death.
- This includes not only pools but also household water sources like bathtubs, toilets, and unattended buckets.
- The ability to initiate CPR immediately after rescue is paramount for improving neurological outcomes.
- Accidental Poisoning and Burns:
- Curiosity drives children to explore, often leading to them ingesting medications, cleaning supplies, or household chemicals.
- Burns can result from hot liquids (scalds), hot stoves, or curling irons.
- First aid training teaches parents how to manage these immediate injuries and provides the critical protocols for securing emergency help and contacting poison control without delay.
By focusing heavily on prevention strategies and immediate intervention for these specific risks, comprehensive courses ensure that parents are not just generally prepared, but specifically prepared for the realities of keeping a child safe in the home environment. They provide the practical skills needed for immediate action when the unexpected occurs.
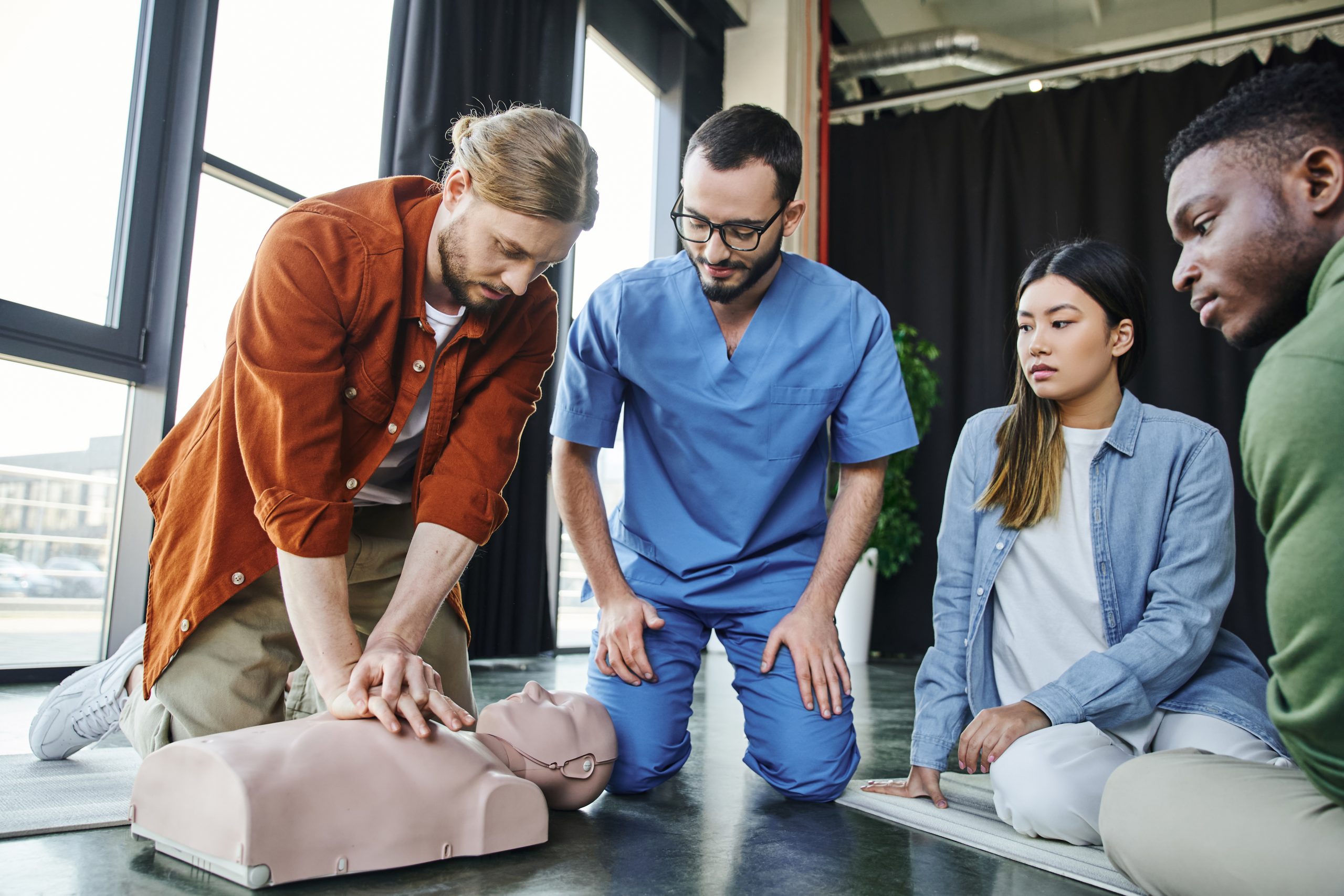
How Does Hands-On Training Build Confidence and Reduce Anxiety?
The distinction between watching a video and physically practicing a skill on a specialized mannequin is the difference between knowing what to do and being able to do it. The ultimate goal of high-quality CPR training is not merely certification, but the cultivation of confidence, which is the single most important factor in a high-stress emergency situation. When panic sets in, trained muscle memory takes over.
Key Benefits of Hands-On, In-Person Instruction:
- Muscle Memory Development: Practicing chest compressions and rescue breaths repeatedly on training manikins builds the kinesthetic memory necessary to act without hesitation.
- Real-Time Feedback: Experienced, local instructors in Raleigh provide immediate corrective feedback on compression depth, rate (100–120 beats per minute, often set to a song rhythm), and hand placement, ensuring techniques are flawless.
- Scenario Simulation: Instructors guide participants through realistic emergency scenarios, such as “unconscious choking infant,” allowing parents to experience the stress and then successfully execute the sequence of back blows, chest thrusts, and subsequent CPR.
- Reduced Decision Paralysis: In a crisis, people often freeze or hesitate. By internalizing the sequence of steps—check the scene, call 911, and begin care—parents can bypass the panic and move directly into the life-saving protocol.
Parents frequently report a significant reduction in general anxiety related to their child’s safety after completing a hands-on course. This sense of preparedness transforms constant worry into rational confidence, allowing them to better enjoy their experience as new parents. They know that if the unthinkable happens, they are not helpless; they are capable of performing the crucial first steps to save their child’s life.

When Is the Ideal Time for Expecting Raleigh Parents to Get Certified?
The best time to take a pediatric CPR and First Aid course is before the baby is born. However, securing this essential training at any time is a worthwhile investment. Many expectant parents prioritize this training in the second or early third trimester, ensuring they are certified and ready before they are sleep-deprived and busy navigating the first few hectic weeks of parenthood.
Key Timing Considerations:
- Be Ready for Day One: Accidents and medical emergencies do not wait for a convenient time. Being certified before you bring your baby home means you are fully prepared from the moment they enter your life.
- Renewal Cycle: AHA certifications are valid for two years. Starting early means your skills are current and refreshed during the critical infant and toddler stages.
- Including the Support Network: It is highly recommended that anyone who will be caring for your child—partners, grandparents, older siblings (if appropriate), and nannies—also receive certification. The class provides an excellent opportunity to learn as a family unit.
- Childcare Requirements: Many high-quality daycare centers and preschools require their staff to hold pediatric CPR and First Aid certification. As a parent, you deserve to hold yourself to the same standard of preparedness.
Classes offered by reputable providers in Raleigh, such as CPR Classes Near Me, ensure that the training is American Heart Association-certified, guaranteeing that your valuable time is spent mastering the most accepted and effective techniques available nationwide. Choosing a provider that offers convenient scheduling and same-day certification maximizes the value for busy new families.
How Can New Parents Ensure They Choose the Highest Quality Training?
Not all CPR and First Aid programs are created equal, and for a skill that might determine your child’s survival, quality is non-negotiable. New parents in Raleigh should look for specific hallmarks of excellence to ensure they receive training that is both effective and professionally accepted.
Qualities of Top-Tier Training for Parents:
- American Heart Association (AHA) Alignment: The AHA is the gold standard in emergency cardiovascular care science and resuscitation education. Choose a local training site that is explicitly aligned with the AHA. This guarantees the curriculum reflects the latest Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) guidelines and is nationally recognized.
- Inclusion of Infant-Specific Modules: The course must go beyond general CPR to include dedicated segments on Infant CPR, Infant choking relief, and the special considerations for pediatric anatomy.
- Guaranteed Hands-On Practice: The class should be entirely in-person or follow a blended format that includes mandatory, verified, in-person skills practice with high-fidelity manikins. Purely online courses are widely rejected by employers and do not provide the necessary muscle memory training.
- Local and Experienced Instructors: Look for local certified trainers who bring real-world experience, often as paramedics, firefighters, or nurses. These professionals can share practical insights and calmly guide you through complex scenarios.
- Efficiency and Convenience: As a new parent, time is precious. Seek providers who offer same-day eCards upon successful completion, allowing you to quickly verify and document your certification without unnecessary administrative delays.
Choosing a trusted local provider, like CPR Classes Near Me in Raleigh, ensures you receive the highest standard of training, making your investment in safety as efficient as it is effective. They provide the certified, local, and professional instruction necessary to face any emergency with clarity and competence.
Conclusion
Parenting is a journey defined by small acts of protection and preparation. While you cannot prevent every scrape or bump, mastering pediatric CPR and First Aid is the single most powerful step you can take to mitigate the risk of a true medical emergency. For new parents in Raleigh, investing a few focused hours in an AHA-certified, hands-on training session provides an invaluable return: the confidence and skill to save your child’s life.
Do not wait for an emergency to realize the necessity of this life-saving knowledge. Equip yourself and your family today with the skills that matter most.
Take the first step toward comprehensive peace of mind. To secure your spot in an upcoming American Heart Association BLS CPR and Pediatric First Aid class designed for new parents in Raleigh, contact CPR Classes Near Me today.
Infant CPR & First Aid: FAQs
What is the difference between Infant CPR and Child CPR?
Infant CPR (for children under 1 year) requires specific modifications due to their smaller and more delicate anatomy. The differences include using only two fingers for compressions (rather than the heel of one hand or two hands for a child), a shallower compression depth (about 1.5 inches), and giving gentler “puffs” for rescue breaths. Child CPR generally applies to ages 1 to puberty.
Is the AHA certification provided accepted by all healthcare providers and childcare facilities?
Yes, the Basic Life Support (BLS) certification issued by an American Heart Association (AHA) Certified Training Site is the most widely recognized and accepted CPR certification nationwide. It is typically the required standard for healthcare professionals, childcare providers, and employers across the United States.
How long does the combined CPR and First Aid class typically take?
The in-person, hands-on component for a comprehensive AHA BLS CPR and First Aid course is approximately 3.7 hours. This duration is standardized to ensure adequate time for all required video modules, skills practice, hands-on demonstrations, and testing. Upon successful completion, you will receive your eCard the same day.
Does this course cover choking relief for infants and children?
Absolutely. A primary component of the pediatric module is hands-on training for conscious and unconscious choking victims across all age groups (infant, child, and adult). This section teaches the specific back blow and chest thrust techniques required for infants.
How often do I need to renew my pediatric CPR certification?
American Heart Association CPR certifications are valid for a period of two years from the date of completion. You can enroll in any BLS or renewal course with CPR Classes Near Me in Raleigh to recertify and maintain your skills.