How to Prepare for a CPR Skills Test: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Passing

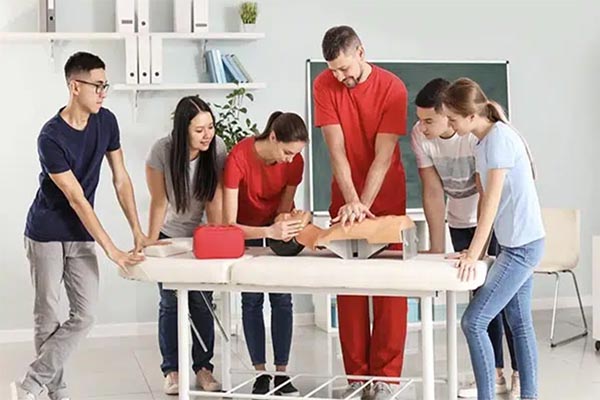
So, you’ve finished the online portion of your CPR course, or maybe you’re gearing up for a full in-person session. Now comes the part that makes many people a little nervous: the CPR skills test.
Think of the skills test as a “practical check-in.” It’s not about tricking you; it’s about making sure that if you ever find yourself in a real-life emergency, your hands know exactly what to do. At CPR Classes Near Me, we want you to walk into that room feeling like a pro.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know to prepare, practice, and pass your CPR skills check on the very first try.
What exactly happens during a CPR skills test?
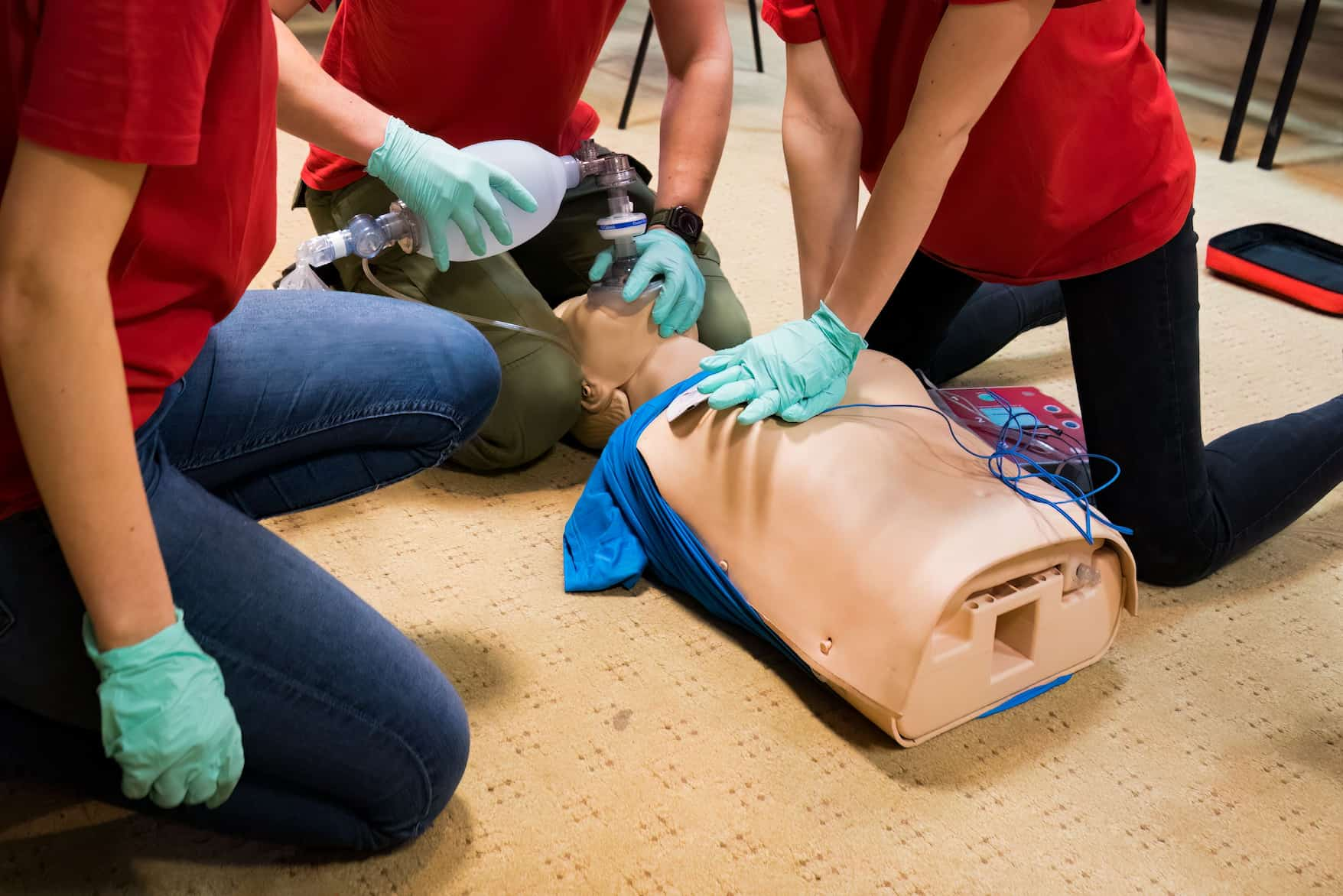
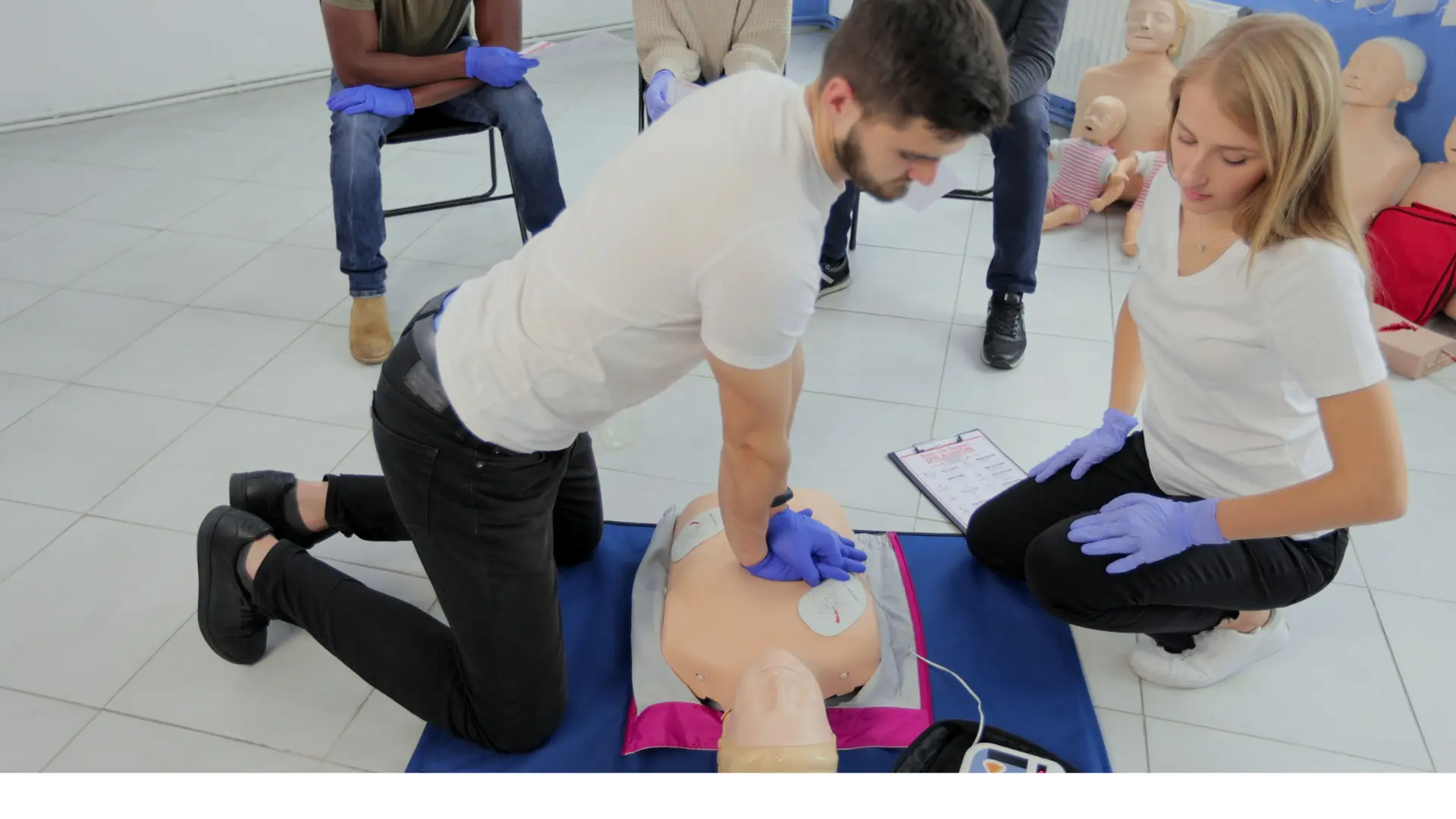
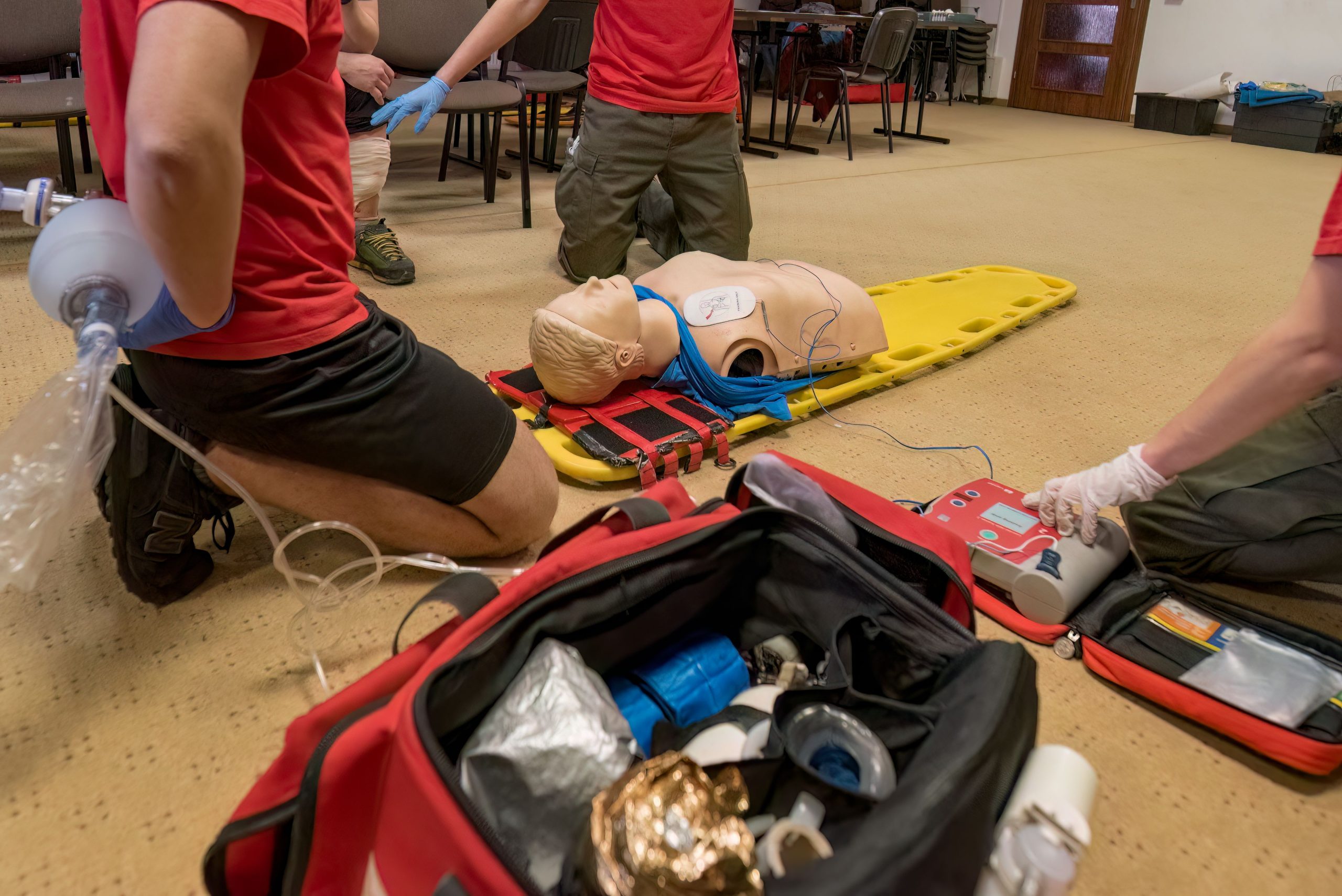
The skills test is a hands-on evaluation where you demonstrate your life-saving abilities to a certified instructor. Unlike the written exam, which tests your “head knowledge,” the skills test evaluates your “muscle memory.”
Typically, the test follows a specific scenario provided by the instructor. You will be asked to:
- Assess the scene for safety.
- Check for responsiveness and breathing.
- Activate emergency services (call 911).
- Perform high-quality chest compressions and rescue breaths on a manikin.
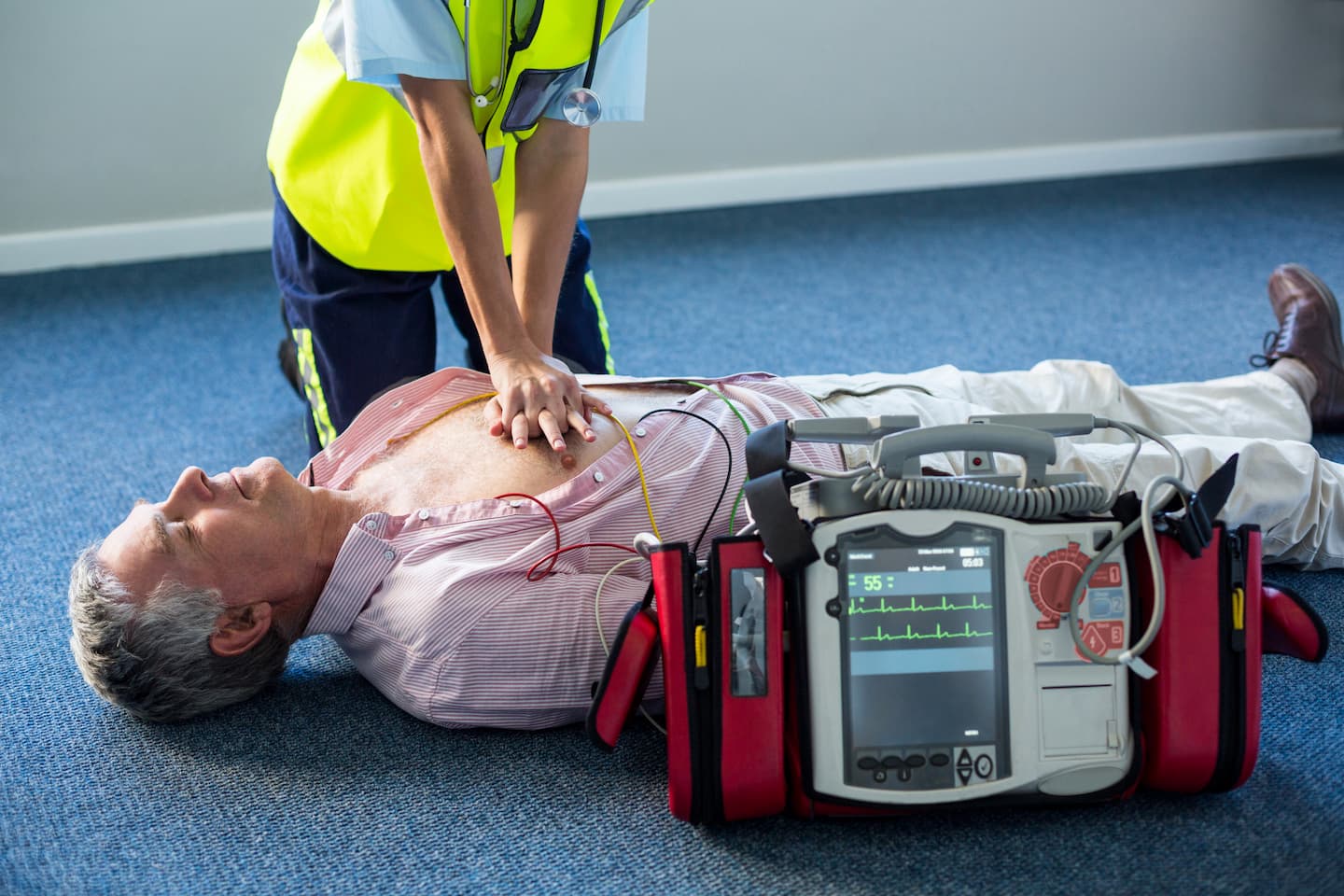
- Correctly use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED).
The instructor uses a standardized checklist—usually from the American Heart Association (AHA) or Red Cross—to mark off each step as you complete it correctly.
How do I prepare my body and mind for the test?
Preparation starts before you even walk through the door. Because CPR is physically demanding, a little bit of physical and mental prep goes a long way.
- Dress for the occasion: You’ll be on your knees on the floor for a good portion of the test. Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes and flat shoes. Avoid skirts or very tight pants.
- Review the “Big Numbers”: Memorize the critical numbers so you don’t have to think about them during the test:
- Rate: 100–120 compressions per minute.
- Depth: At least 2 inches for adults.
- Ratio: 30 compressions to 2 breaths (for single-rescuer adult CPR).
- Visualize the flow: Close your eyes and run through the “Check-Call-Care” sequence. Visualizing yourself successfully completing the steps reduces anxiety.
What are the keys to high-quality chest compressions?
Compressions are the most important part of the test. Instructors look for “high-quality CPR,” which means you aren’t just pushing; you’re pushing effectively.
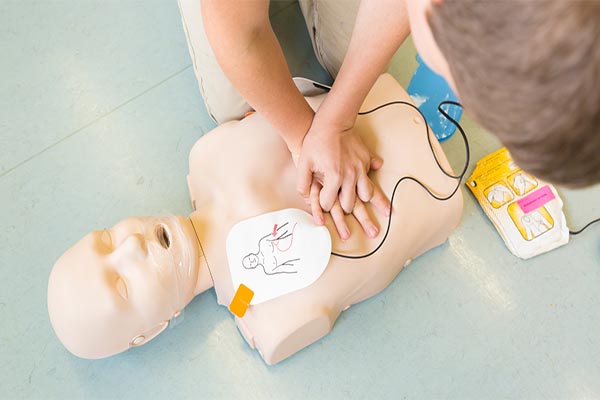
- Hand Placement: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest (lower half of the breastbone) and the other hand on top.
- Body Mechanics: Lock your elbows and position your shoulders directly over your hands. Use your body weight to push, not just your arm muscles. This prevents fatigue.
- Allow Full Recoil: This is a big one! After every push, let the chest come all the way back up to its normal position. If you “lean” on the chest, the heart can’t refill with blood.
- The “Stayin’ Alive” Rhythm: Aim for 100–120 beats per minute. Pushing too fast is just as ineffective as pushing too slowly.
How do I master the rescue breathing portion?
Rescue breaths are often where students lose points, usually because they are rushed. To pass this section, focus on these details:
- Open the Airway: Use the head-tilt/chin-lift maneuver. If the airway isn’t open, the air won’t go in.
- Seal the Barrier: Whether you’re using a pocket mask or a face shield, ensure it’s airtight.
- Watch for Chest Rise: Give each breath over 1 second. You should see the manikin’s chest physically rise. If it doesn’t, reposition the head and try one more time.
- Don’t Over-Ventilate: Only give enough air to see the chest rise. Blowing too hard can actually be harmful.
What is the correct way to use an AED during the test?
The AED is a “set it and forget it” device, but you have to follow its instructions perfectly. In a skills test, the instructor wants to see that you can integrate the AED without stopping CPR for too long.
- Turn it on immediately: As soon as the AED arrives, power it on.
- Follow the prompts: The device will tell you exactly when to attach pads, when to stay clear, and when to push the shock button.
- Clear the victim: Loudly and clearly shout “Clear!” and look to ensure no one is touching the manikin before the AED analyzes or delivers a shock.
- Resume CPR: Immediately after a shock (or if “no shock advised”), start compressions again. Don’t wait for the instructor to tell you to start.
What are the most common mistakes that lead to failure?
Even the best students can make simple mistakes under the pressure of a stopwatch. Here is what to avoid:
- Forgetting to call 911: It sounds silly, but many people jump straight into compressions and forget to “activate the emergency response system.”
- Shallow compressions: If you don’t hit that 2-inch depth, the blood isn’t reaching the brain.
- Taking too long between cycles: Interruptions in compressions should be less than 10 seconds. This includes the time it takes to give breaths.
- Leaning: Failing to let the chest recoil fully is a common reason for “Needs Remediation.”
How can I practice without a manikin at home?
While you need a manikin for the official check, you can practice the “flow” anywhere.
- Use a Pillow: While it doesn’t offer the same resistance, practicing your hand placement and rhythm on a firm pillow helps with muscle memory.
- Use a Metronome: Download a free metronome app and set it to 110 bpm. Practice tapping your hands to that beat until it feels natural.
- Verbalize the Steps: Practice saying out loud, “The scene is safe. Are you okay? Call 911!” This helps solidify the sequence in your mind.
Conclusion
Preparing for a CPR skills test is all about confidence and consistency. Remember, the instructor wants you to pass! They are there to ensure you are a capable link in the “Chain of Survival.” By focusing on high-quality compressions, mastering the AED prompts, and keeping your rhythm steady, you’ll be ready to handle any scenario thrown your way.
Ready to get certified? Whether you’re a first-timer or need a renewal, CPR Classes Near Me makes it easy to find high-quality, local training that fits your schedule. Don’t wait until an emergency happens—get the skills you need today.
Contact CPR Classes Near Me today to find a skills check location near you!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What happens if I fail the CPR skills test?
A: Don’t panic! If you don’t pass a specific skill, most instructors provide “remediation.” This means they will coach you on what went wrong and allow you to practice and try again during the same session. The goal is competency, not perfection on the first try.
Q: Do I have to give mouth-to-mouth during the test?
A: Most modern CPR classes use barrier devices like pocket masks or face shields. You are generally not required to have direct mouth-to-mouth contact with the manikin. In some “Hands-Only CPR” sessions, rescue breaths might be skipped entirely, but for a full certification, you will demonstrate breaths using a barrier.
Q: How long does the skills check take?
A: If you have already completed the online coursework (blended learning), the in-person skills check usually takes between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on the number of students in the class.
Q: Is there a written test too?
A: Yes, most certification levels (like BLS or Heartsaver) require both a written exam (usually multiple choice) and a physical skills test. You typically need a score of 80% or higher to pass the written portion.
Q: Can I wear my watch or jewelry during the test?
A: It’s best to remove large watches or dangling bracelets, as they can get caught or be uncomfortable when you are performing deep chest compressions.