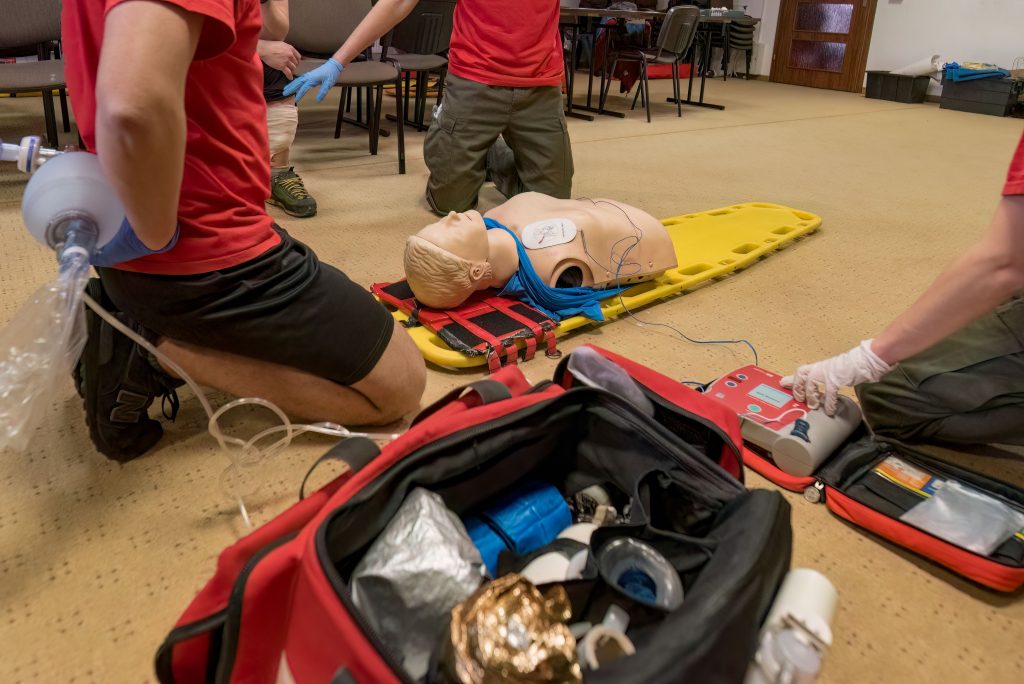
Sports are not only a fantastic way to maintain physical fitness and mental well-being, but they also foster teamwork, discipline, and resilience. However, the physical demands of sports can sometimes lead to injuries, which can range from minor cuts and bruises to more serious conditions like fractures and concussions. Whether you’re a professional athlete, a college player, or someone who enjoys sports as a hobby, having a basic understanding of first aid for sports injuries is crucial. This knowledge can significantly influence recovery outcomes, reduce downtime, and protect your long-term health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore essential first aid techniques that every athlete should master to handle common sports injuries effectively.
Before diving into the specifics of first aid, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the different types of injuries that can occur during sports activities. Sports injuries are often classified into two main categories, each requiring a different approach to treatment and management:
Knowing the difference between acute and chronic injuries is fundamental in applying the correct first aid treatment. It also aids in determining whether immediate medical attention is necessary or if the injury can be managed with rest and care at home.
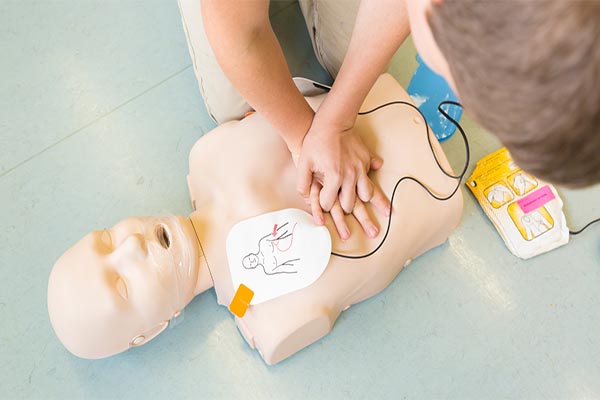
First aid in sports is not merely a helpful skill; it is a critical component of an athlete’s toolkit. The primary goals of first aid are to minimize the severity of an injury, prevent further harm, and expedite the healing process. Immediate and appropriate care can also significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications, such as chronic pain or decreased mobility, which might otherwise hinder an athlete’s ability to perform or enjoy their sport.
Understanding basic first aid principles is essential for providing effective care in the event of a sports injury. Here are the fundamental principles every athlete should know:
Every athlete should be equipped with the knowledge of essential first aid techniques to manage common sports injuries effectively. These techniques are designed to provide immediate relief and prevent the injury from worsening:
The R.I.C.E. method is a time-tested and widely recommended first aid technique for managing acute injuries, such as sprains and strains. It stands for:
For cuts, abrasions, or any open wounds, it is important to act quickly to prevent infection and promote healing:
Suspected fractures or dislocations require careful handling to avoid further injury:
Screenshot
Head injuries, even minor ones, require prompt and careful attention due to the risk of serious complications:
While first aid knowledge is invaluable, prevention remains the best strategy to avoid sports injuries altogether. Implementing preventive measures can greatly reduce the incidence and severity of injuries, allowing athletes to enjoy their activities safely:
While first aid is critical for immediate care, certain situations demand professional medical evaluation and intervention. Knowing when to seek help can prevent complications and ensure proper healing:
A well-stocked first aid kit is an essential tool for athletes, providing the means to respond to injuries quickly and effectively. Here are the key items to include in a comprehensive sports first aid kit:
First aid in sports is an indispensable skill for athletes of all levels. By understanding sports injuries and learning essential first aid techniques, athletes can effectively manage injuries and promote quicker recovery. It is important to recognize that while first aid provides immediate relief, knowing when to seek professional medical help is equally vital to ensure a safe return to your favorite activities. Stay prepared, stay safe, and enjoy the game. With the right knowledge and tools, athletes can protect their health and continue to pursue the sports they love with confidence and peace of mind.
Don’t wait until an emergency happens! Equip yourself with the essential skills to respond effectively to sports injuries and other emergencies. Contact CPR Classes Near Me today to enroll in CPR and First Aid classes. Gain the confidence and knowledge to make a difference in critical situations. Your preparedness can save lives—sign up now!
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!