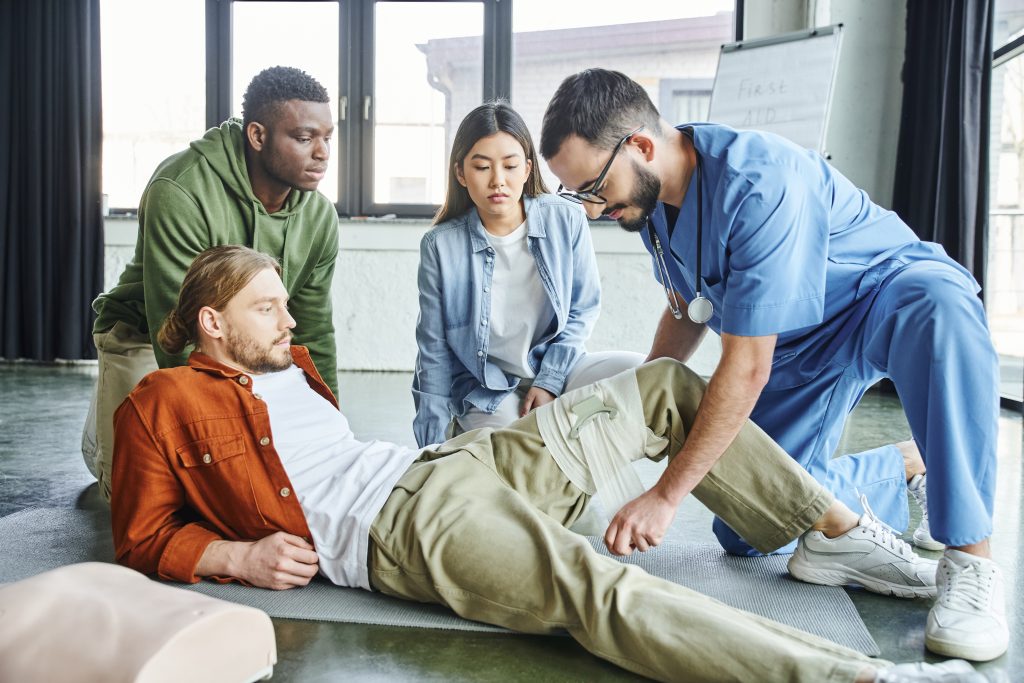

Accidents can happen anytime and anywhere, leaving us unprepared and panicked. One of the most critical situations you might encounter is severe bleeding, which requires immediate attention. Knowing how to effectively administer first aid can make the difference between life and death. This article provides you with essential information on handling severe bleeding emergencies.
Severe bleeding, also known as hemorrhaging, occurs when a large amount of blood is lost from the body. This can result from various causes, including deep cuts, puncture wounds, or traumatic injuries. Understanding the severity of the situation is crucial for effective first aid.

When you encounter severe bleeding, it’s vital to act quickly and efficiently. Follow these steps to provide immediate assistance:
Before you begin administering first aid, ensure that emergency services are on the way. Dial your local emergency number and provide the dispatcher with as much information as possible about the situation.
Safety first! Use protective gloves if available to reduce the risk of infection for both you and the injured person. If gloves are not available, try to use a barrier like a plastic bag or cloth.
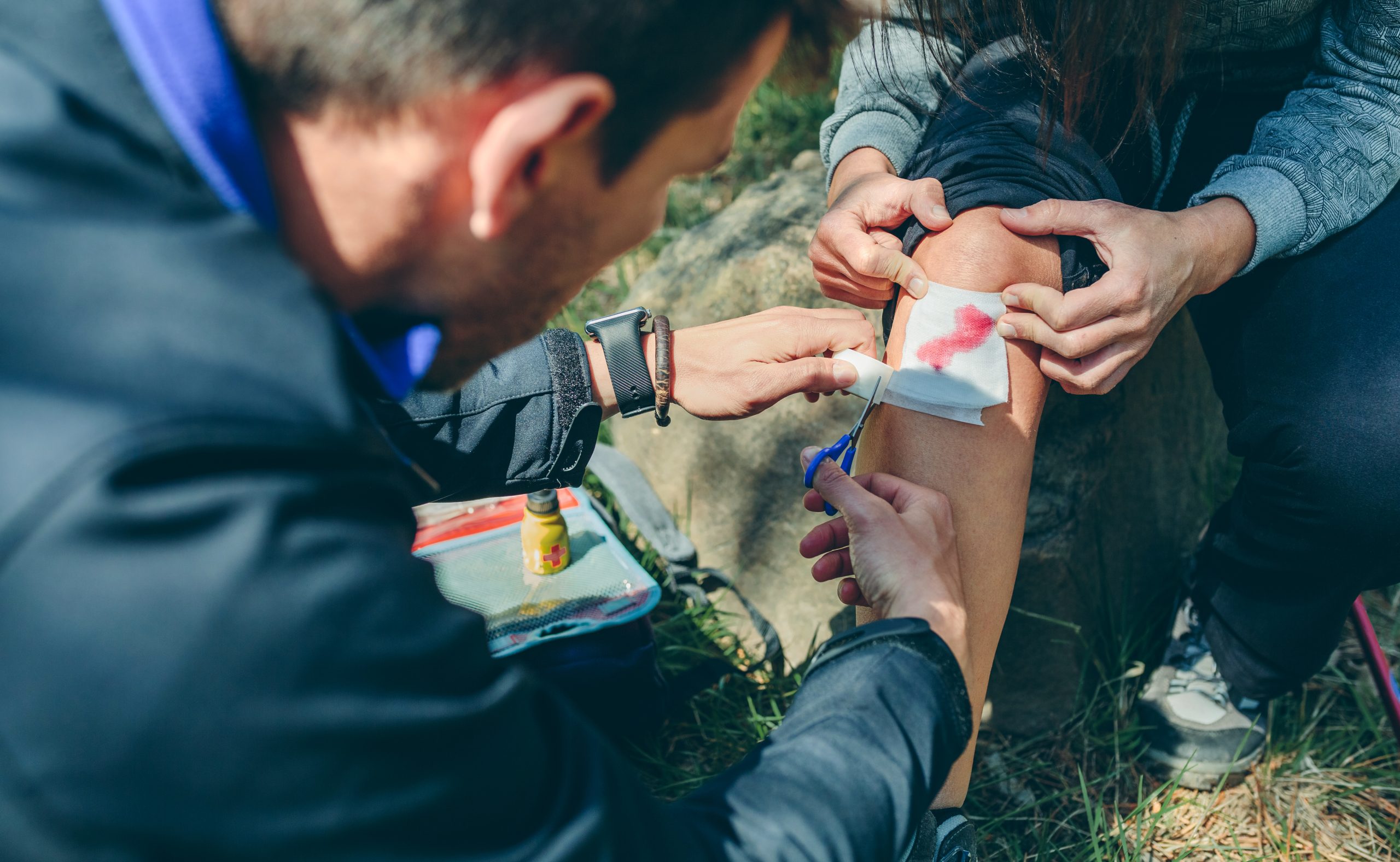
Firmly press on the wound using a clean cloth, bandage, or your hand. Maintain steady pressure to help control the bleeding. If the cloth becomes soaked with blood, do not remove it. Instead, add more layers and continue applying pressure.
If possible, raise the injured area above the level of the heart. Elevation can help slow down the bleeding by reducing blood flow to the wound site.
Once the bleeding has slowed or stopped, secure the dressing in place with a bandage or adhesive tape. Ensure that it is snug but not too tight, as this could cut off circulation.
Keep the injured person calm and monitor their condition. Look out for signs of shock, such as pale skin, rapid breathing, or confusion. If you notice any of these symptoms, lay the person down, cover them with a blanket, and continue to reassure them until help arrives.
While the above steps are essential for immediate care, there are additional techniques you can employ if you have the necessary training and resources.
A tourniquet is a device used to apply pressure to a limb to restrict blood flow. It should only be used when direct pressure fails to stop the bleeding, and the injury is life-threatening. Place the tourniquet above the wound, tighten until bleeding stops, and note the time it was applied to inform medical personnel.
Hemostatic agents are substances that promote blood clotting and can be used in conjunction with direct pressure. These are often found in first aid kits designed for trauma situations.
Once the bleeding is under control, it’s important to focus on preventing infection. Clean the area around the wound with soap and water, avoiding the wound itself. Apply an antiseptic ointment if available, and ensure the dressing is changed regularly to maintain hygiene.
A closeup of medical professionals performing CPR on a mannequin on the floor
While first aid can stabilize an injury, professional medical treatment is often necessary for severe bleeding. Seek immediate help if:
Knowing how to administer first aid for severe bleeding can save lives. Remember to stay calm, act quickly, and follow the steps outlined in this guide. By being prepared and informed, you can make a significant difference in an emergency situation.
Keep a well-stocked first aid kit at home, in your car, and at work to ensure you’re ready to handle any situation that arises. Regularly refresh your knowledge and consider taking a first aid course to build confidence and skills.
In emergencies, every second counts. By understanding the basics of first aid for severe bleeding, you’re equipped to be a vital first responder when it’s needed most.
Don’t wait until an emergency happens! Equip yourself with the knowledge and skills to save lives by enrolling in CPR and First Aid classes. Contact CPR Classes Near Me today to find a course that fits your schedule and location. Being prepared can make all the difference in critical situations. Act now and become a confident first responder!
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!