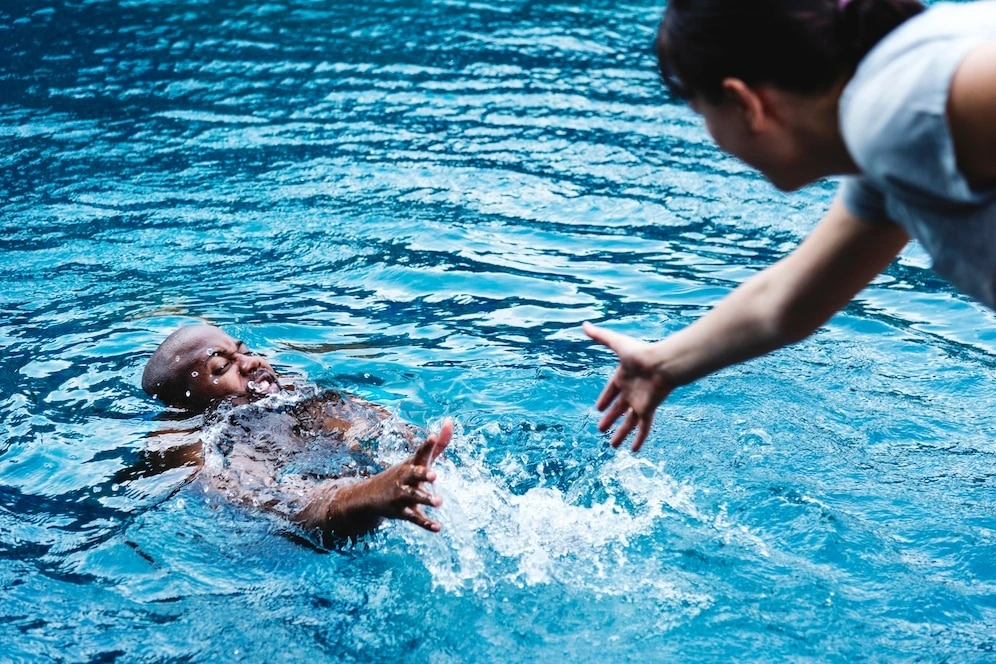

Drowning is a serious and often fatal emergency that requires immediate action. Knowing how to perform CPR on drowning victims can be the difference between life and death. In this article, we’ll explore the essential steps and special considerations for administering CPR in drowning situations.
Understanding the basic principles of CPR for drowning victims is crucial for anyone who spends time near water, whether at the beach, pool, or on a boat. With this knowledge, you can be prepared to act swiftly and confidently in an emergency.
Drowning occurs when a person is unable to breathe due to submersion in water. This can lead to a lack of oxygen in the body, causing serious damage to the brain and other organs. Drowning can happen quickly, often in just a few minutes, and can occur in any body of water, from oceans and lakes to swimming pools and bathtubs.
When a person is submerged, water can enter the airways, blocking the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This leads to a decrease in oxygen levels in the blood and an increase in carbon dioxide, causing the victim to lose consciousness. If not addressed immediately, this can result in brain damage or death.
Certain factors increase the risk of drowning, such as lack of swimming skills, not wearing life jackets, and alcohol consumption near water. Children are particularly at risk, and adults supervising them should be vigilant. Understanding these risk factors can help prevent potential drowning incidents.
Drowning is often silent, with victims unable to call for help. Look for signs such as head low in the water, gasping for air, or mouth at water level. Recognizing these subtle signs can prompt quicker intervention, potentially saving a life.
Drowning incidents can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics and implications for treatment.
Dry drowning occurs when water does not actually enter the lungs. Instead, the vocal cords spasm and close up, making it difficult to breathe. This can happen immediately after submersion or even after leaving the water.
Wet drowning happens when water enters the lungs, causing the person to struggle for air and potentially leading to lung damage. This is the most common type of drowning and typically requires immediate intervention with rescue breaths to expel water.
Secondary drowning occurs when water is inhaled into the lungs and causes inflammation or edema, often hours after the initial incident. Symptoms may include coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It’s crucial to monitor victims closely, even after they seem to have recovered.
CPR, or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, is a life-saving technique that helps maintain blood flow and oxygen to the brain and heart during emergencies. In drowning cases, CPR is particularly vital because it helps restore breathing and circulation until professional medical help arrives.
In drowning situations, the primary issue is lack of oxygen due to water in the lungs. Therefore, rescue breaths are prioritized to help expel water and deliver oxygen. This differs from other cardiac emergencies where chest compressions are emphasized.
Bystanders often play a critical role in drowning emergencies. Immediate action, such as calling emergency services and beginning CPR, can significantly impact the victim’s chances of survival. Training bystanders in CPR and water safety can improve outcomes in such incidents.
Witnessing or responding to a drowning can be traumatic. It’s important for rescuers and bystanders to seek support if needed. Debriefing and counseling can help process the experience and prepare for future emergencies.
When performing CPR on a drowning victim, there are a few special considerations to keep in mind.
Unlike standard CPR, where chest compressions are emphasized, CPR for drowning victims should prioritize rescue breaths. This helps expel water from the lungs and restore breathing. Giving effective breaths can be challenging, so it’s essential to create a good seal over the victim’s mouth.
Drowning victims are often exposed to cold water, which can lead to hypothermia. Hypothermia can complicate resuscitation efforts, so it’s crucial to keep the person warm with blankets or towels while performing CPR. Be mindful of the environment and remove wet clothing if possible.
If the victim is a child, use a gentler approach with smaller breaths and lighter compressions. Children’s bodies are more fragile, and excessive force can cause injury. Knowing how to modify techniques for children can improve the effectiveness of CPR.
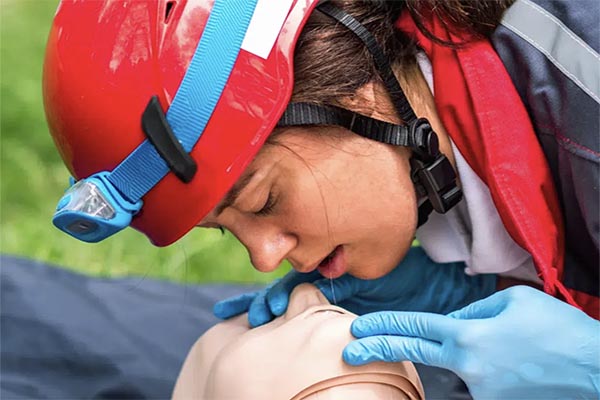

Before approaching the victim, ensure that the scene is safe for both you and the victim. Remove the person from the water and assess the situation. Be cautious of potential hazards, such as strong currents or slippery surfaces, that could put you at risk.
Gently tap the victim and ask if they are okay. Look for signs of breathing by observing the chest for movement. If the person is unresponsive and not breathing, or only gasping, call for emergency medical help immediately. Quick assessment can save valuable time.
Place the person on their back on a firm, flat surface. This position allows for effective compressions and rescue breaths. Ensure the head is not tilted too far back to avoid obstructing the airway.
Tilt the head back slightly and lift the chin to open the airway. Be gentle, especially with children, to prevent further injury. This step is crucial for ensuring that the rescue breaths are effective.
Pinch the nose shut, cover the person’s mouth with yours, and give two full breaths. Each breath should last about one second and make the chest rise. If the chest does not rise, reposition the head and try again.
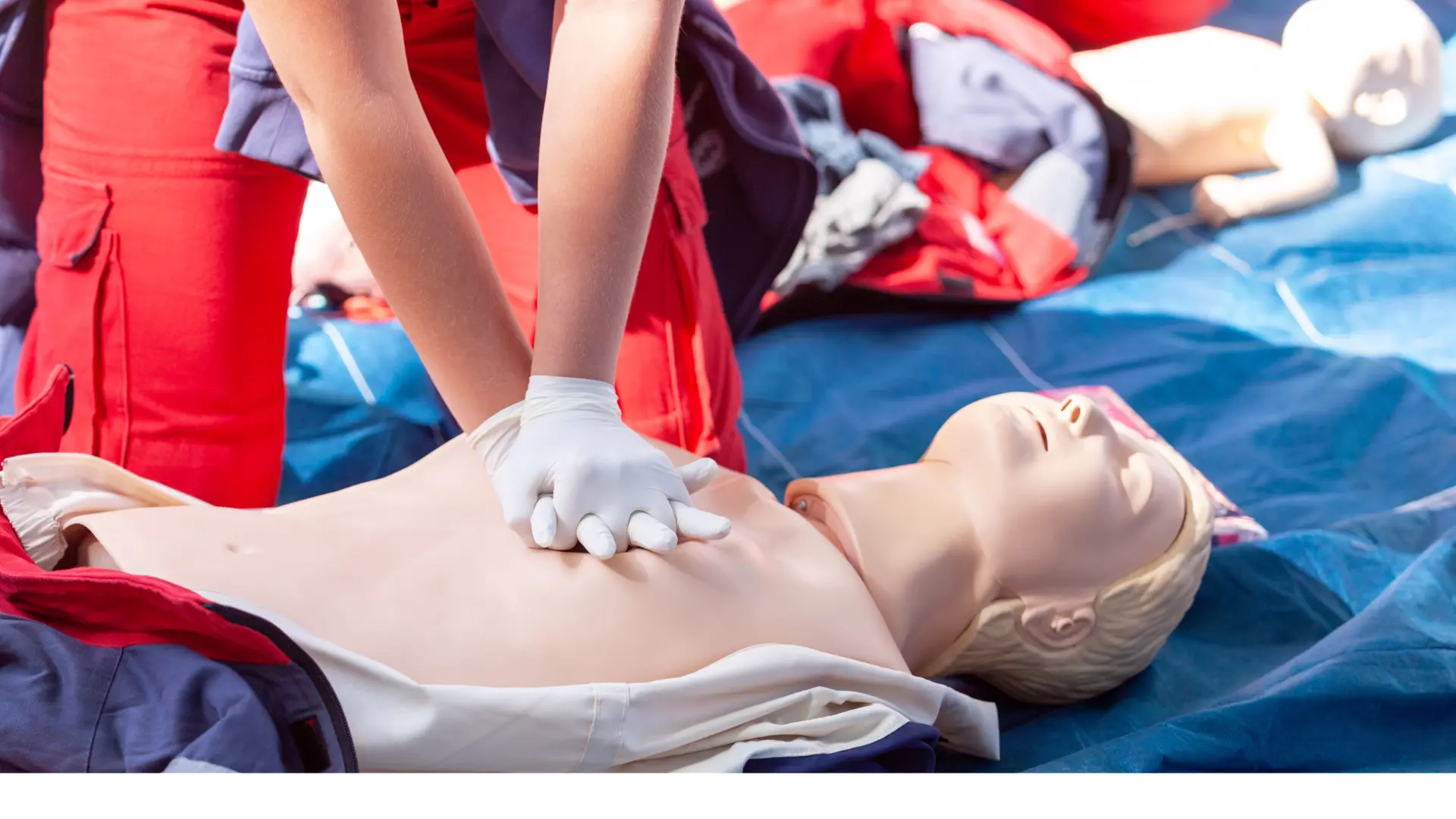
Place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, just below the nipples. Put your other hand on top and interlock your fingers. Correct hand placement ensures that compressions are effective.
Press down hard and fast, allowing the chest to rise fully between compressions. Aim for a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. Consistent rhythm and depth are crucial for maintaining blood flow.
Alternate between 30 chest compressions and two rescue breaths until the victim shows signs of life, such as coughing or breathing, or until emergency personnel arrive. Persistence is key, as resuscitation can take time.
Once the victim has been stabilized and professional help has arrived, they may still require additional medical attention.
Even if the victim regains consciousness, they should be monitored for any delayed symptoms of respiratory distress. Medical professionals may conduct tests to ensure there is no further damage to the lungs or brain.
Survivors of drowning incidents may experience trauma or anxiety related to the event. Providing psychological support and counseling can aid in their recovery and help them return to normal activities.
Education and awareness are key to preventing future drowning incidents. Encourage water safety education, swimming lessons, and the use of life jackets to reduce the risk of drowning. Empowering communities with knowledge can save lives.
Don’t wait until it’s too late! Equip yourself with the life-saving skills needed to respond effectively in emergencies. Contact CPR Classes Near Me today to enroll in CPR and First Aid classes. Whether you’re a parent, caregiver, or simply someone who wants to be prepared, our comprehensive training will empower you to act confidently in critical situations.
Take the first step towards becoming a lifesaver—reach out now!
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!