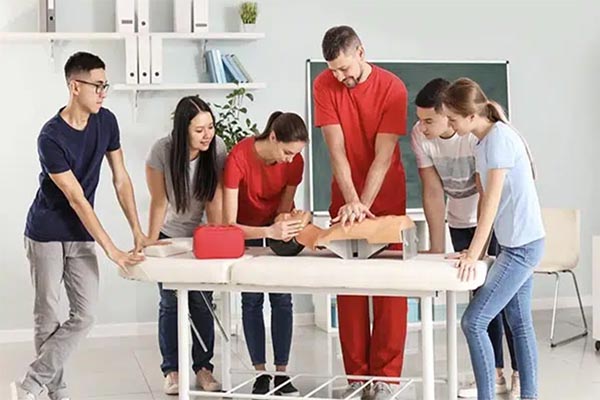

When emergencies strike, quick action can be the difference between life and death. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a critical skill that can save lives, but did you know that the way you perform CPR differs depending on whether you’re aiding an infant or an adult? Understanding these differences is crucial, as each demographic requires distinct techniques due to their anatomical and physiological differences. The necessity of these variations becomes evident when considering the potential consequences of applying incorrect methods, which can range from ineffective resuscitation to severe physical harm.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between infant and adult CPR, why these variations are essential, and how you can be prepared to perform CPR effectively in any situation. Whether you’re a parent, a caregiver, or an individual committed to being prepared for emergencies, understanding these nuances can make a significant difference in critical moments.
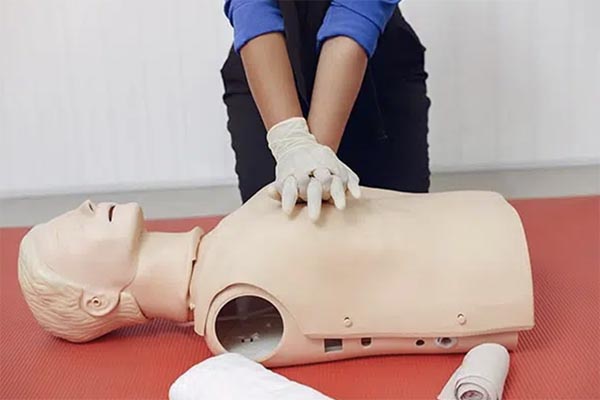
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique used in emergencies when someone’s heartbeat or breathing has stopped. The main goal of CPR is to restore partial flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and heart. This can help delay tissue death and extend the window of opportunity for a successful resuscitation without permanent brain damage. CPR is a foundational component of first aid, and its efficacy can be the deciding factor in the survival and recovery of an individual experiencing cardiac arrest.
Before diving into the differences, it’s important to understand the basic steps of CPR, which generally include:
These steps are universal, but the technique varies significantly between infants and adults. The differences in execution are tailored to account for the distinct anatomical structures and physiological needs of each age group.
The American Heart Association provides specific guidelines for different age groups, and it’s crucial to follow these tailored approaches to increase the chance of survival and reduce the risk of injury. Each age group presents unique challenges and requirements, emphasizing the importance of age-appropriate CPR techniques.
Infants, defined as children under one year old, have different body structures compared to adults. Their bones are more flexible, and their organs are more fragile. Additionally, infants have a smaller lung capacity, meaning they require gentler rescue breaths. This fragility necessitates a delicate approach to avoid causing harm during resuscitation efforts.
In contrast, adults have a more robust skeletal structure and larger lung capacity, necessitating more forceful compressions and breaths during CPR. The increased physical resilience of adults allows for more vigorous intervention without the same risk of injury present in infants.
For adults, CPR compressions should be at least two inches deep and performed with both hands interlocked, placed on the lower half of the sternum. This depth is crucial for effectively circulating blood through the adult body, which requires a certain amount of force to overcome the resistance of the chest cavity.
For infants, use only two fingers placed just below the nipple line. Compressions should be about 1.5 inches deep. This gentler approach ensures you don’t cause injury to the infant’s delicate bones and organs. The reduced depth and force reflect the infant’s smaller size and fragility.
When giving rescue breaths to adults, ensure the airway is open by tilting the head back and lifting the chin. Pinch the nose shut and give two breaths, watching for chest rise. This technique ensures that air is effectively delivered into the lungs, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream.
For infants, be extra gentle. Cover the infant’s mouth and nose with your mouth, and give two gentle breaths, just enough to see the chest rise. Remember, infants have a much smaller lung capacity, so less air is needed. The emphasis is on delicacy to prevent overinflating the lungs, which could cause injury.
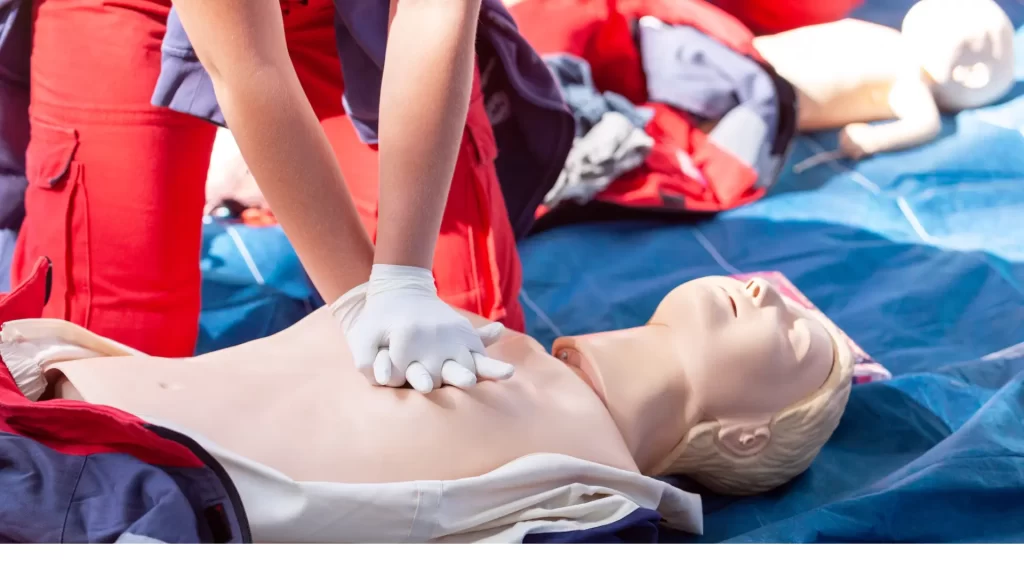
Understanding and applying the correct CPR technique is crucial. Incorrect application can lead to injuries, such as broken ribs in adults or more severe damage in infants. Furthermore, the effectiveness of CPR can be compromised if the technique is not suited to the individual’s size and age. The consequences of improper technique highlight the critical need for appropriate training and awareness.
For adults, the main concern is applying enough pressure to be effective without causing injury. Proper technique ensures that compressions are effective in maintaining circulation without causing unnecessary harm. In infants, the risk is even greater due to their fragility. Using adult CPR techniques on an infant can cause significant harm, including broken bones and internal injuries. The potential for injury underscores the importance of adjusting techniques based on the victim’s age and size.
Applying the correct CPR technique improves the chances of survival significantly. Studies show that prompt, correctly performed CPR can double or triple a cardiac arrest victim’s chances of survival. This demonstrates that knowledge and skill can make a profound difference in life-and-death situations. The ability to perform age-appropriate CPR effectively can ensure that vital oxygen reaches the brain and heart, sustaining life until advanced medical care is available.
Pediatric CPR is not just for infants. It also includes children up to puberty. While the technique is similar to adult CPR, there are adjustments based on the child’s size and development. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone responsible for the care of children, as it ensures that the intervention is both effective and safe.
For children, use one or two hands for chest compressions, depending on the size of the child. The depth of compressions should be about two inches. This ensures that the compressions are adequate to maintain circulation without being overly forceful. Rescue breaths should be gentler compared to adults but stronger than those for infants. These modifications take into account the developing anatomy and physiology of children, balancing the need for effective resuscitation with the risk of injury.
It’s crucial to be trained in pediatric CPR if you are a parent, caregiver, or someone who frequently interacts with children. Regular practice ensures you maintain your skills and can respond swiftly and effectively in an emergency. Training courses offer hands-on experience, allowing individuals to practice on manikins that simulate the size and structure of children and infants. This practical experience is invaluable in building confidence and competence in performing CPR.
CPR is a skill that requires practice. Many organizations, such as the American Heart Association and the Red Cross, offer CPR certification courses that cover both infant and adult CPR. These courses often include hands-on practice with manikins, which is invaluable for understanding the correct pressure and technique. Certification courses are designed to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform CPR effectively in real-world situations.
In addition to in-person training, online resources and video tutorials can be helpful for learning and refreshing your CPR skills. However, they should not replace formal training, which provides the opportunity for feedback and correction. Online materials can serve as a supplemental tool to reinforce learning and ensure that techniques remain sharp between certification renewals.
CPR guidelines can change, and skills can fade over time. It’s recommended to renew your CPR certification every two years to stay updated on the latest techniques and guidelines. Regular refreshers ensure that your knowledge remains current and that you are prepared to respond effectively in an emergency. Staying informed about updates in CPR protocols is crucial, as advancements in medical understanding can lead to changes that improve outcomes.
Understanding the differences between infant and adult CPR is not just a matter of technique; it’s a matter of life and death. By applying the appropriate method for the situation, you increase the chances of a successful outcome and reduce the risk of harm. The distinction between age-appropriate techniques highlights the importance of tailored approaches to emergency care, ensuring that interventions are both effective and safe.
Whether you’re a parent, caregiver, or just a responsible citizen, investing time in learning CPR is a valuable commitment to the safety and well-being of those around you. Remember, in an emergency, the right skills can save a life. Stay prepared, stay informed, and make a difference. Your knowledge and readiness to act can be a critical lifeline in a moment of crisis, underscoring the power of preparedness and the impact of informed action.
Don’t wait for an emergency to learn how to save a life. Enrolling in CPR and First Aid classes is a proactive step you can take to ensure you’re prepared for any situation. Whether you’re a parent, caregiver, or simply someone who wants to be ready to help, these classes provide essential skills and knowledge.
Take the first step towards becoming a lifesaver. Sign up for a CPR and First Aid class today!
Our primary goal is to ensure that you receive a top-quality CPR/First Aid certification. With our in-person training in Austin, you can learn CPR and BLS in just one class. Your presence is all that’s needed to continue with your lesson! During your session, you will complete all the live-training components necessary to ensure you receive your AHA Healthcare Provider certification card.
Our CPR Classes in Austin are discounted to $59.95 (saving you $20), and our CPR + First Aid Class is offered at $79.95 (also saving you $20). When looking for CPR Classes, ensure to check for the American Heart Association seal. Other sites might seem cheaper but frequently lack the official training credentials demanded by employers.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will obtain a CPR certification that is valid for two years. The AHA CPR certification is recognized with the highest acceptance rate among employers nationwide.
Indeed! Enroll in any CPR Certification Austin BLS course to extend your certification for an additional two years. The in-person BLS course and the Renewal Class are identical.
Anyone capable of completing the course independently should consider pursuing CPR training and CPR Certification. There is no minimum age restriction for obtaining a CPR certification in Austin through the American Heart Association (AHA)..
CPR training needs to be carried out in person to guarantee its effectiveness. Our experienced instructors offer an engaging and dynamic learning experience. Typically, employers do not recognize CPR certifications that are obtained solely through online courses.
All authorized American Heart Association training centers are obligated to display the entire video. After a three-hour session with CPR Classes Near Me Austin, your BLS CPR eCard will be promptly issued by the instructor on the same day!